Local nasal specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 20525156
- PMCID: PMC2876180
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-2-3-117
Local nasal specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis
Abstract
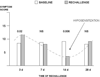
The possibility of producing local hyposensitization by administering allergens via mucosal routes was envisaged at the beginning of 1900, and local nasal immunotherapy has been extensively studied since the 1970s. Presently, there are 21 randomized controlled trials being conducted with the most common allergens, consistently showing the clinical efficacy of local nasal immunotherapy for rhinitis. Other advantages are that it has an optimal safety profile and can be self-administered at home by the patient. Moreover, there are several data from animal models and from humans that confirm the immunomodulatory effect of intranasally administered antigens. On the other hand, local nasal immunotherapy seems to be effective only on rhinitis symptoms and requires a particular technique of administration. For these reasons, its clinical use is progressively declining in favour of the sublingual route although nasal immunotherapy is validated in official documents and remains a viable alternative to injection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Noninjection routes for immunotherapy.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 Mar;111(3):437-48; quiz 449. doi: 10.1067/mai.2003.129. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12642818 Review.
-
Non-injection routes for allergen immunotherapy: focus on sublingual immunotherapy.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006 Jan;5(1):43-51. doi: 10.2174/187152806775269286. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16613563 Review.
-
Safety of allergen-specific sublingual immunotherapy and nasal immunotherapy.Chem Immunol Allergy. 2003;82:109-18. doi: 10.1159/000071545. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2003. PMID: 12947997 Review.
-
[Comparison of injection-related and local immunotherapy].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2003 Jun;14(84):695-9. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2003. PMID: 14524308 Review. Polish.
-
Local nasal immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022 Dec;12(12):1503-1516. doi: 10.1002/alr.23011. Epub 2022 May 23. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022. PMID: 35543418
Cited by
-
Breaking the mold: nontraditional approaches to allergen immunotherapy for environmental allergens.Immunotherapy. 2024;16(18-19):1153-1169. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2024.2408216. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Immunotherapy. 2024. PMID: 39382452 Review.
-
Review: The Nose as a Route for Therapy. Part 2 Immunotherapy.Front Allergy. 2021 Jul 1;2:668781. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2021.668781. eCollection 2021. Front Allergy. 2021. PMID: 35387044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal administration of regulatory dendritic cells is useful for the induction of nasal mucosal tolerance in a mice model of allergic rhinitis.World Allergy Organ J. 2020 Aug 11;13(8):100447. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100447. eCollection 2020 Aug. World Allergy Organ J. 2020. PMID: 32817781 Free PMC article.
-
Modified allergens and their potential to treat allergic disease.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014 Dec;14(12):478. doi: 10.1007/s11882-014-0478-9. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014. PMID: 25269402 Review.
-
Novel therapeutic targets for allergic airway disease in children.Drugs Context. 2019 Jul 9;8:212590. doi: 10.7573/dic.212590. eCollection 2019. Drugs Context. 2019. PMID: 31391855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Noon L. Prophylactic inoculation against hay fever. Lancet. 1911;i:1572–3.
-
- Black JH. The oral administration of pollen. J Lab Clin Med. 1927;12:1156.
-
- Black JH. The oral administration of pollen: clinical report. J Lab Clin Med. 1928;13:709.
-
- Herxeimer H. Bronchial hypersensitization and hyposensitization in man. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1951;40:40–57. - PubMed
-
- Herxeimer H, Prior EN. Further observations in induced asthma and bronchial hyposensitization. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1952;3:159–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

