Pharmacological studies of the mechanism and function of interleukin-1beta-induced miRNA-146a expression in primary human airway smooth muscle
- PMID: 20525168
- PMCID: PMC2894768
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-68
Pharmacological studies of the mechanism and function of interleukin-1beta-induced miRNA-146a expression in primary human airway smooth muscle
Abstract
Background: Despite the widespread induction of miR-146a during the innate immune response little is known regarding its biogenesis, function and mechanism. We have therefore examined the role of miR-146a during the interleukin (IL)-1beta-stimulated IL-6 and IL-8 release and proliferation in primary human airway smooth muscle (HASM) cells.
Methods: HASM cells were isolated from human lung re-section, cultured to a maximum of 3 - 6 passages and then exposed to IL-1beta. miR-146a expression were determined by qRT-PCR, IL-6 and IL-8 release by ELISA and proliferation using bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. The role of NF-kappaB and the MAP kinase pathways was assessed using pharmacological inhibitors of IKK2 (TPCA-1), JNK (SP600125), p38 MAP kinase (SB203580) and MEK-1/2 (PD98059). miR-146a function was determined following transfection of HASM with inhibitors and mimics using Amaxa electroporation.
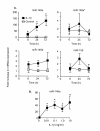
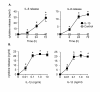
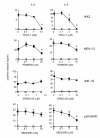
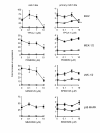
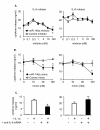
Results: IL-1beta induced a time-dependent and prolonged 100-fold induction in miR-146a expression, which correlated with release of IL-6 and IL-8. Exposure to IL-1beta had no effect upon HASM proliferation. Pharmacological studies showed that expression of primary miR-146a was regulated at the transcriptional levels by NF-kappaB whilst post-transcriptional processing to mature miR-146a was regulated by MEK-1/2 and JNK-1/2. Functional studies indicated that IL-1beta-induced miR-146a expression does not negatively regulate IL-6 and IL-8 release or basal proliferation. However, inhibition of IL-1beta-induced IL-6 and IL-8 release was observed at the super-maximal intracellular miR-146a levels obtained by transfection with miR-146a mimics and indicates that studies using miRNA mimics can produce false positive results. Mechanistic studies showed that in the presence of super-maximal levels, the action of miR-146a mimics was mediated at a step following IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA transcription and not through down-regulation of IL-1 receptor associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1) and TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) protein expression, two predicted miR-146a targets involved in IL-1beta signalling.
Conclusions: We have shown that IL-1beta-induced miR-146a expression in HASM and that this was regulated at the transcriptional level by NF-kappaB and at the post-transcriptional level by the MEK-1/2 and JNK-1/2. Unlike previous reports, studies using miRNA inhibitors showed that miR-146a expression did not regulate IL-6 and IL-8 release or proliferation and suggest miR-146a function and mechanism is cell-type dependent.
Figures
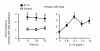




Similar articles
-
Divergent intracellular pathways regulate interleukin-1beta-induced miR-146a and miR-146b expression and chemokine release in human alveolar epithelial cells.FEBS Lett. 2009 Oct 20;583(20):3349-55. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.09.038. Epub 2009 Sep 26. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19786024
-
Different signal pathways regulate IL-1β-induced mature and primary miRNA-146a expression in human alveolar epithelial cells.Acta Physiol Hung. 2014 Sep;101(3):282-90. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.101.2014.3.3. Acta Physiol Hung. 2014. PMID: 25183503
-
Interleukin-1beta induces MMP-9 expression via p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathways in human tracheal smooth muscle cells.J Cell Physiol. 2007 Jun;211(3):759-70. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20992. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17311279
-
MiRNA-146a-A Key Player in Immunity and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 14;24(16):12767. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612767. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miRNA-146a in the regulation of the innate immune response and cancer.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Dec;36(Pt 6):1211-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0361211. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 19021527 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-181a regulates inflammation responses in monocytes and macrophages.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058639. Epub 2013 Mar 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23516523 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptors in Cystic Fibrosis: Impact of Dysfunctional microRNA on Innate Immune Responses in the Cystic Fibrosis Lung.J Innate Immun. 2016;8(6):541-549. doi: 10.1159/000444687. Epub 2016 Apr 5. J Innate Immun. 2016. PMID: 27043239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-29a reduces TIMP-1 production by dermal fibroblasts via targeting TGF-β activated kinase 1 binding protein 1, implications for systemic sclerosis.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 30;9(12):e115596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115596. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25549087 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reduced expression of miR-146a in human bronchial epithelial cells alters neutrophil migration.Clin Transl Allergy. 2019 Nov 27;9:62. doi: 10.1186/s13601-019-0301-8. eCollection 2019. Clin Transl Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31798831 Free PMC article.
-
Airway smooth muscle in airway reactivity and remodeling: what have we learned?Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Dec;305(12):L912-33. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00259.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24142517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

