The role of transposable elements in the evolution of non-mammalian vertebrates and invertebrates
- PMID: 20525173
- PMCID: PMC2911107
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-r59
The role of transposable elements in the evolution of non-mammalian vertebrates and invertebrates
Abstract
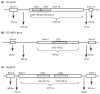
Background: Transposable elements (TEs) have played an important role in the diversification and enrichment of mammalian transcriptomes through various mechanisms such as exonization and intronization (the birth of new exons/introns from previously intronic/exonic sequences, respectively), and insertion into first and last exons. However, no extensive analysis has compared the effects of TEs on the transcriptomes of mammals, non-mammalian vertebrates and invertebrates.
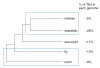
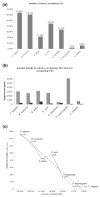
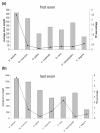
Results: We analyzed the influence of TEs on the transcriptomes of five species, three invertebrates and two non-mammalian vertebrates. Compared to previously analyzed mammals, there were lower levels of TE introduction into introns, significantly lower numbers of exonizations originating from TEs and a lower percentage of TE insertion within the first and last exons. Although the transcriptomes of vertebrates exhibit significant levels of exonization of TEs, only anecdotal cases were found in invertebrates. In vertebrates, as in mammals, the exonized TEs are mostly alternatively spliced, indicating that selective pressure maintains the original mRNA product generated from such genes.
Conclusions: Exonization of TEs is widespread in mammals, less so in non-mammalian vertebrates, and very low in invertebrates. We assume that the exonization process depends on the length of introns. Vertebrates, unlike invertebrates, are characterized by long introns and short internal exons. Our results suggest that there is a direct link between the length of introns and exonization of TEs and that this process became more prevalent following the appearance of mammals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transposable elements in disease-associated cryptic exons.Hum Genet. 2010 Feb;127(2):135-54. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0752-4. Epub 2009 Oct 10. Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 19823873
-
Molecular phylogeny of the antiangiogenic and neurotrophic serpin, pigment epithelium derived factor in vertebrates.BMC Genomics. 2006 Oct 4;7:248. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-248. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 17020603 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of transposed element insertion within human and mouse genomes reveals Alu's unique role in shaping the human transcriptome.Genome Biol. 2007;8(6):R127. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-6-r127. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 17594509 Free PMC article.
-
Exonization of transposed elements: A challenge and opportunity for evolution.Biochimie. 2011 Nov;93(11):1928-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.014. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21787833 Review.
-
Transposable element influences on gene expression in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017 Jan;1860(1):157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017. PMID: 27235540 Review.
Cited by
-
Transposon-derived and satellite-derived repetitive sequences play distinct functional roles in Mammalian intron size expansion.Evol Bioinform Online. 2012;8:301-19. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S9758. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Evol Bioinform Online. 2012. PMID: 22807622 Free PMC article.
-
Taming, Domestication and Exaptation: Trajectories of Transposable Elements in Genomes.Cells. 2021 Dec 20;10(12):3590. doi: 10.3390/cells10123590. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of 5Mg chromosome of Aegilops geniculata and 5Uu chromosome of Aegilops umbellulata reveal genic diversity in the tertiary gene pool.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jul 13;14:1144000. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1144000. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37521926 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic sequence around butterfly wing development genes: annotation and comparative analysis.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023778. Epub 2011 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21909358 Free PMC article.
-
The Developmental Gene Hypothesis for Punctuated Equilibrium: Combined Roles of Developmental Regulatory Genes and Transposable Elements.Bioessays. 2020 Feb;42(2):e1900173. doi: 10.1002/bies.201900173. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Bioessays. 2020. PMID: 31943266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, Funke R, Gage D, Harris K, Heaford A, Howland J, Kann L, Lehoczky J, LeVine R, McEwan P, McKernan K, Meldrim J, Mesirov JP, Miranda C, Morris W, Naylor J, Raymond C, Rosetti M, Santos R, Sheridan A, Sougnez C. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. doi: 10.1038/35057062. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, Rogers J, Abril JF, Agarwal P, Agarwala R, Ainscough R, Alexandersson M, An P, Antonarakis SE, Attwood J, Baertsch R, Bailey J, Barlow K, Beck S, Berry E, Birren B, Bloom T, Bork P, Botcherby M, Bray N, Brent MR, Brown DG, Brown SD, Bult C, Burton J, Butler J, Campbell RD, Carninci P, Cawley S. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520–562. doi: 10.1038/nature01262. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

