Copine A plays a role in the differentiation of stalk cells and the initiation of culmination in Dictyostelium development
- PMID: 20525180
- PMCID: PMC2890595
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-59
Copine A plays a role in the differentiation of stalk cells and the initiation of culmination in Dictyostelium development
Abstract
Background: Copines are calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins found in diverse eukaryotic organisms. We are studying the function of copines in Dictyostelium discoideum, a single-celled amoeba that undergoes cell differentiation and morphogenesis to form multicellular fruiting bodies when placed in starvation conditions. Previously, we showed that Dictyostelium cells lacking the copine A (cpnA) gene are not able to complete the developmental cycle, arresting at the slug stage. The aim of this study is to further characterize the developmental defect of the cpnA- cells.
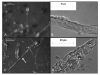
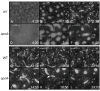
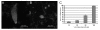
Results: Time-lapse imaging revealed that cpnA- cells exhibited delayed aggregation and made large mounds that formed one large slug as compared to the smaller slugs of the wild-type cells. While the prespore cell patterning appeared to be normal within the cpnA- slugs, the prestalk cell patterning was different from wild-type. When cpnA- cells were mixed with a small percentage of wild-type cells, chimeric fruiting bodies with short stalks formed. When a small percentage of cpnA- cells was mixed with wild-type cells, the cpnA- cells labeled with GFP were found located throughout the chimeric slug and in both the stalk and sporehead of the fruiting bodies. However, there appeared to be a small bias towards cpnA- cells becoming spore cells. When cpnA- cells were developed in buffer containing EGTA, they were also able to differentiate into either stalk or spore cells to form fruiting bodies with short stalks.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that CpnA is involved in the regulation of aggregation, slug size, and culmination during Dictyostelium development. More specifically, CpnA appears to be involved in the function and differentiation of prestalk cells and plays a role in a calcium-regulated signaling pathway critical to triggering the initiation of culmination.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Copine A is expressed in prestalk cells and regulates slug phototaxis and thermotaxis in developing Dictyostelium.Dev Growth Differ. 2011 Oct;53(8):948-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2011.01300.x. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Dev Growth Differ. 2011. PMID: 21950343 Free PMC article.
-
Copine A is required for cytokinesis, contractile vacuole function, and development in Dictyostelium.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Mar;6(3):430-42. doi: 10.1128/EC.00322-06. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17259548 Free PMC article.
-
Copine A, a calcium-dependent membrane-binding protein, transiently localizes to the plasma membrane and intracellular vacuoles in Dictyostelium.BMC Cell Biol. 2005 Dec 12;6:46. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-6-46. BMC Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16343335 Free PMC article.
-
The control of chemotactic cell movement during Dictyostelium morphogenesis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000 Jul 29;355(1399):983-91. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0634. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000. PMID: 11128992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Dictyostelium morphogenesis by cAMP-dependent protein kinase.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993 Jun 29;340(1293):305-13. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0072. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993. PMID: 8103933 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic AMP signaling in Dictyostelium promotes the translocation of the copine family of calcium-binding proteins to the plasma membrane.BMC Cell Biol. 2018 Jul 16;19(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12860-018-0160-5. BMC Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30012091 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of prognostic value, immune implication and biological function of CPNE1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Apr 3;11:1157269. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1157269. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37077419 Free PMC article.
-
Copine A is expressed in prestalk cells and regulates slug phototaxis and thermotaxis in developing Dictyostelium.Dev Growth Differ. 2011 Oct;53(8):948-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2011.01300.x. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Dev Growth Differ. 2011. PMID: 21950343 Free PMC article.
-
Copine A Interacts with Actin Filaments and Plays a Role in Chemotaxis and Adhesion.Cells. 2019 Jul 21;8(7):758. doi: 10.3390/cells8070758. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31330887 Free PMC article.
-
Copine A regulates the size and exocytosis of contractile vacuoles and postlysosomes in Dictyostelium.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 Jun;10(6):979-994. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12874. Epub 2020 May 19. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 32351039 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

