Tobramycin at subinhibitory concentration inhibits the RhlI/R quorum sensing system in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa environmental isolate
- PMID: 20525206
- PMCID: PMC2898818
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-148
Tobramycin at subinhibitory concentration inhibits the RhlI/R quorum sensing system in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa environmental isolate
Abstract
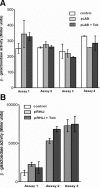
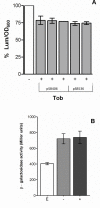
Background: Antibiotics are not only small molecules with therapeutic activity in killing or inhibiting microbial growth, but can also act as signaling molecules affecting gene expression in bacterial communities. A few studies have demonstrated the effect of tobramycin as a signal molecule on gene expression at the transcriptional level and its effect on bacterial physiology and virulence. These have shown that subinhibitory concentrations (SICs) of tobramycin induce biofilm formation and enhance the capabilities of P. aeruginosa to colonize specific environments.
Methods: Environmental P. aeruginosa strain PUPa3 was grown in the presence of different concentrations of tobramycin and it was determined at which highest concentration SIC, growth, total protein levels and translation efficiency were not affected. At SIC it was then established if phenotypes related to cell-cell signaling known as quorum sensing were altered.
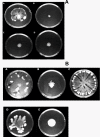
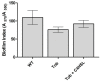
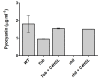
Results: In this study it was determined whether tobramycin sensing/response at SICs was affecting the two independent AHL QS systems in an environmental P. aeruginosa strain. It is reasonable to assume that P. aeruginosa encounters tobramycin in nature since it is produced by niche mate Streptomyces tenebrarius. It was established that SICs of tobramycin inhibited the RhlI/R system by reducing levels of C4-HSL production. This effect was not due to a decrease of rhlI transcription and required tobramycin-ribosome interaction.
Conclusions: Tobramycin signaling in P. aeruginosa occurs and different strains can have a different response. Understanding the tobramycin response by an environmental P. aeruginosa will highlight possible inter-species signalling taking place in nature and can possible also have important implications in the mode of utilization for human use of this very important antibiotic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A rhlI 5' UTR-Derived sRNA Regulates RhlR-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2019 Oct 8;10(5):e02253-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02253-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31594819 Free PMC article.
-
Bismuth-thiol incorporation enhances biological activities of liposomal tobramycin against bacterial biofilm and quorum sensing molecules production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Pharm. 2009 May 21;373(1-2):141-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.02.001. Epub 2009 Feb 12. Int J Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19429299
-
Extracellular DNA release, quorum sensing, and PrrF1/F2 small RNAs are key players in Pseudomonas aeruginosa tobramycin-enhanced biofilm formation.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019 May 23;5(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41522-019-0088-3. eCollection 2019. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019. PMID: 31149345 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin inhibits biofilm formation, attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence and enhances Pseudomonas aeruginosa clearance in a mouse peritoneal implant infection model.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 28;12(4):e0176883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176883. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28453568 Free PMC article.
-
Marine-derived quorum-sensing inhibitory activities enhance the antibacterial efficacy of tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Mar Drugs. 2014 Dec 24;13(1):1-28. doi: 10.3390/md13010001. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25546516 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Alterations of growth rate and gene expression levels of UPEC by antibiotics at sub-MIC.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018 Jul;63(4):451-457. doi: 10.1007/s12223-017-0582-z. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2018. PMID: 29327292
-
Effect of Micro-Patterned Mucin on Quinolone and Rhamnolipid Profiles of Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa under Antibiotic Stress.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 13;9(1):150-161. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00519. Epub 2022 Dec 20. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36538577 Free PMC article.
-
Cephalosporins Interfere With Quorum Sensing and Improve the Ability of Caenorhabditis elegans to Survive Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 28;12:598498. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.598498. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33584609 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-Inhibitory Antibiotic Exposure and Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Nov 13;10(11):1393. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10111393. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem and piperacillin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxA and exoS transcriptional expression.New Microbes New Infect. 2019 Oct 8;32:100608. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2019.100608. eCollection 2019 Nov. New Microbes New Infect. 2019. PMID: 31719997 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

