Phenotype and functional changes of Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes in Behçet's disease and the effect of infliximab on Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cell expansion, activation and cytotoxicity
- PMID: 20525258
- PMCID: PMC2911900
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3043
Phenotype and functional changes of Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes in Behçet's disease and the effect of infliximab on Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cell expansion, activation and cytotoxicity
Abstract
Introduction: Infliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) that has been introduced recently for Behçet's disease (BD) patients who were resistant to standard treatment. The aim of this study was to analyse the functional changes of Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes in both active and inactive disease and the effect of infliximab on Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cell expansion, activation and cytotoxicity.
Methods: We investigated 1) cell expansion, 2) expression of TNFRII receptor, 3) perforin and gamma interferon (IFN) content, 4) release of granzyme A (GrA) and 5) phenotype changes, in vitro and in vivo, in Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes by means of fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis of lymphocyte cultures from patients with active and inactive BD and healthy subjects.
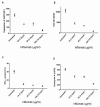
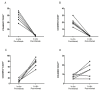
Results: Cell expansion, expression of TNFRII, perforin and gamma IFN content and release of granzyme A were significantly higher in active patients. In vitro and ex vivo treatment with infliximab resulted in a significant reduction of all parameters together with changes in the phenotype of Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cells.
Conclusions: All together these data indicate that infliximab is capable of interfering with Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cell function in BD and although cell culture models cannot reliably predict all potential effects of the drug in vivo, our results present the possibility that this drug may find use in a range of immunological disorders, characterized by dysregulated cell-mediated immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes in Italian patients with Behçet's disease: evidence for expansion, and tumour necrosis factor receptor II and interleukin-12 receptor beta1 expression in active disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(5):R262-8. doi: 10.1186/ar785. Epub 2003 Jun 30. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003. PMID: 12932289 Free PMC article.
-
Pentoxifylline inhibits Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocyte activation of patients with active Behçets disease in vitro.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2007 Jul-Sep;20(3):601-6. doi: 10.1177/039463200702000318. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17880773
-
Blocking TNF in vitro with infliximab determines the inhibition of expansion and interferon gamma production of Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes from patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. A role in the susceptibility to tuberculosis?Reumatismo. 2009 Jan-Mar;61(1):21-6. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2009.21. Reumatismo. 2009. PMID: 19370184
-
Non-peptide antigens activating human Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T lymphocytes.Immunol Lett. 2004 Sep;95(2):129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.06.013. Immunol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15388252 Review.
-
γδ T-APCs: a novel tool for immunotherapy?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Jul;68(14):2443-52. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0706-6. Epub 2011 May 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21573785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gamma Delta (γδ) T Cells and Their Involvement in Behçet's Disease.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:705831. doi: 10.1155/2015/705831. Epub 2015 Oct 11. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26539557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biologics, colchicine, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and interferon-alpha for Neuro-Behçet's Syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(12):CD010729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010729.pub2. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25521793 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the nature of human γδ T cells: a biographical sketch of the highly empathetic.Cell Mol Immunol. 2013 Jan;10(1):21-9. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2012.44. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Cell Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23085947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behçet's syndrome pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets.Intern Emerg Med. 2014 Apr;9(3):257-65. doi: 10.1007/s11739-013-1036-5. Epub 2014 Jan 12. Intern Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 24415351 Review.
-
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Intestinal Behçet's Disease.Gut Liver. 2018 Nov 15;12(6):623-632. doi: 10.5009/gnl17462. Gut Liver. 2018. PMID: 29788675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giardina A, Ferrante A, Ciccia F, Vadalà M, Giardina E, Triolo G. One year study of efficacy and safety of infliximab in the treatment of patients with ocular and neurological Behçet's disease refractory to standard immunosuppressive drugs. Rheumatol Int. 2009. in press . - PubMed
-
- Kahan A, Hamzaoui K, Ayed K. Abnormalities of T lymphocyte subsets in Behçet' s disease demonstrated with anti-CD45RA and anti-CD29 monoclonal antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1992;19:742–746. - PubMed
-
- Todaro M, Zerilli M, Triolo G, Iovino F, Patti M, Accardo-Palumbo A, di Gaudio F, Turco MC, Petrella A, de Maria R, Stassi G. NF-kappaB protects Behçet's disease T cells against CD95-induced apoptosis up-regulating antiapoptotic proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2179–2191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

