Heat shock protein 90 in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 20525284
- PMCID: PMC2896944
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-24
Heat shock protein 90 in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
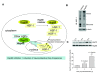
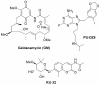
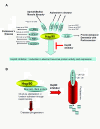
Hsp90 is a molecular chaperone with important roles in regulating pathogenic transformation. In addition to its well-characterized functions in malignancy, recent evidence from several laboratories suggests a role for Hsp90 in maintaining the functional stability of neuronal proteins of aberrant capacity, whether mutated or over-activated, allowing and sustaining the accumulation of toxic aggregates. In addition, Hsp90 regulates the activity of the transcription factor heat shock factor-1 (HSF-1), the master regulator of the heat shock response, mechanism that cells use for protection when exposed to conditions of stress. These biological functions therefore propose Hsp90 inhibition as a dual therapeutic modality in neurodegenerative diseases. First, by suppressing aberrant neuronal activity, Hsp90 inhibitors may ameliorate protein aggregation and its associated toxicity. Second, by activation of HSF-1 and the subsequent induction of heat shock proteins, such as Hsp70, Hsp90 inhibitors may redirect neuronal aggregate formation, and protect against protein toxicity. This mini-review will summarize our current knowledge on Hsp90 in neurodegeneration and will focus on the potential beneficial application of Hsp90 inhibitors in neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Translational Shift of HSP90 as a Novel Therapeutic Target from Cancer to Neurodegenerative Disorders: An Emerging Trend in the Cure of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases.Curr Drug Metab. 2017;18(9):868-876. doi: 10.2174/1389200218666170728115606. Curr Drug Metab. 2017. PMID: 28758577 Review.
-
Heat shock protein 90 in Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:796869. doi: 10.1155/2014/796869. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25374890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of heat-shock protein 90 in maintaining and facilitating the neurodegenerative phenotype in tauopathies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 29;104(22):9511-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701055104. Epub 2007 May 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17517623 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of Hsp90 chaperone expression protects against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity in PC12 cells.J Mol Neurosci. 2014 Mar;52(3):392-402. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0163-9. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24234033
-
The yeast Hsp110 family member, Sse1, is an Hsp90 cochaperone.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):26654-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.38.26654. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10480867
Cited by
-
The complexity of tau in Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Jul 13;705:183-194. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.04.022. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31028844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of redox signaling in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:484613. doi: 10.1155/2013/484613. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24455696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures of Hsp90α and Hsp90β bound to a purine-scaffold inhibitor reveal an exploitable residue for drug selectivity.Proteins. 2019 Oct;87(10):869-877. doi: 10.1002/prot.25750. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Proteins. 2019. PMID: 31141217 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oxidative Damage in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015;2015:504678. doi: 10.1155/2015/504678. Epub 2015 Aug 2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015. PMID: 26301043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and genomic architecture of the evolution of resistance to antifungal drug combinations.PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003390. Epub 2013 Apr 4. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23593013 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

