Mapping of quantitative trait loci for flesh colour and growth traits in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)
- PMID: 20525320
- PMCID: PMC2900243
- DOI: 10.1186/1297-9686-42-17
Mapping of quantitative trait loci for flesh colour and growth traits in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)
Abstract
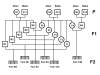
Background: Flesh colour and growth related traits in salmonids are both commercially important and of great interest from a physiological and evolutionary perspective. The aim of this study was to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) affecting flesh colour and growth related traits in an F2 population derived from an isolated, landlocked wild population in Norway (Byglands Bleke) and a commercial production population.
Methods: One hundred and twenty-eight informative microsatellite loci distributed across all 29 linkage groups in Atlantic salmon were genotyped in individuals from four F2 families that were selected from the ends of the flesh colour distribution. Genotyping of 23 additional loci and two additional families was performed on a number of linkage groups harbouring putative QTL. QTL analysis was performed using a line-cross model assuming fixation of alternate QTL alleles and a half-sib model with no assumptions about the number and frequency of QTL alleles in the founder populations.
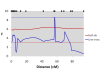
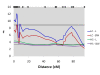
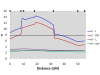
Results: A moderate to strong phenotypic correlation was found between colour, length and weight traits. In total, 13 genome-wide significant QTL were detected for all traits using the line-cross model, including three genome-wide significant QTL for flesh colour (Chr 6, Chr 26 and Chr 4). In addition, 32 suggestive QTL were detected (chromosome-wide P < 0.05). Using the half-sib model, six genome-wide significant QTL were detected for all traits, including two for flesh colour (Chr 26 and Chr 4) and 41 suggestive QTL were detected (chromosome-wide P < 0.05). Based on the half-sib analysis, these two genome-wide significant QTL for flesh colour explained 24% of the phenotypic variance for this trait.
Conclusions: A large number of significant and suggestive QTL for flesh colour and growth traits were found in an F2 population of Atlantic salmon. Chr 26 and Chr 4 presented the strongest evidence for significant QTL affecting flesh colour, while Chr 10, Chr 5, and Chr 4 presented the strongest evidence for significant QTL affecting growth traits (length and weight). These QTL could be strong candidates for use in marker-assisted selection and provide a starting point for further characterisation of the genetic components underlying flesh colour and growth.
Figures


References
-
- Gjerde B, Schaeffer LR. Body traits in rainbow trout: II. Estimates of heritabilities and of phenotypic and genetic correlations. Aquaculture. 1989;80:25–44. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(89)90271-8. - DOI
-
- Quinton CD, McMillan I, Glebe BD. Development of an Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) genetic improvement program: Genetic parameters of harvest body weight and carcass quality traits estimated with animal models. Aquaculture. 2005;247:211–217. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.02.030. - DOI
-
- Iwamoto RN, Myers JM, Hershberger WK. Heritability and genetic correlations for flesh coloration in pen-reared coho salmon. Aquaculture. 1990;86:181–190. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(90)90111-Y. - DOI
-
- Torissen OJ, Hardy RW, Shearer KD. Pigmentation of salmonids- carotenoid deposition and metabolism. Crit Rev Aquat Sci. 1989;1:209–225.
-
- Nickell DC, Bromage NR. The effect of timing and duration of feeding astaxanthin on the development and variation of fillet colour and efficiency of pigmentation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Aquaculture. 1998;169:233–246. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00385-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

