Anterior gradient-2 plays a critical role in breast cancer cell growth and survival by modulating cyclin D1, estrogen receptor-alpha and survivin
- PMID: 20525379
- PMCID: PMC2917027
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2586
Anterior gradient-2 plays a critical role in breast cancer cell growth and survival by modulating cyclin D1, estrogen receptor-alpha and survivin
Abstract
Introduction: Anterior-gradient 2 (AGR2) is an estrogen-responsive secreted protein. Its upregulation has been well documented in a number of cancers, particularly breast cancer, for which mixed data exist on the prognostic implications of AGR2 expression. Although emerging evidence indicates that AGR2 is associated with poor prognosis, its function and impact on cancer-relevant pathways have not been elucidated in breast cancer.
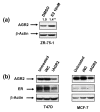
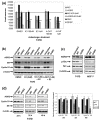
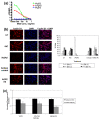
Methods: To investigate the biologic role of AGR2 in breast cancer, AGR2 was transiently knocked down, by using siRNA, in T47 D and ZR-75-1 (estrogen receptor-alpha (ER)-positive) and MDA-MB-231 and SK-BR-3 (ER-negative) human breast cancer cell lines. The impact of silencing AGR2 was evaluated in both anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent growth (soft agar, spheroid) assays. Cell-cycle profiles in ER-positive cell lines were determined with BrdU incorporation, and cell death was measured with Annexin V, JC-1, and F7-26 staining. After transiently silencing AGR2 or stimulating with recombinant AGR2, modulation of key regulators of growth and survival pathways was assessed with Western blot. Combination studies of AGR2 knockdown with the antiestrogens tamoxifen and fulvestrant were carried out and assessed at the level of anchorage-dependent growth inhibition and target modulation (cyclin D1, ER).
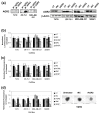
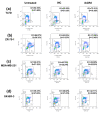
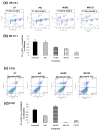
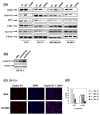
Results: AGR2 knockdown inhibited growth in anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent assays, with a more-pronounced effect in ER-positive cell lines. Cyclin D1 levels and BrdU incorporation were reduced with AGR2 knockdown. Conversely, cyclin D1 was induced with recombinant AGR2. AGR2 knockdown induced cell death in ZR-75-1 and T47 D cells, and also downregulated survivin and c-Myc. Evidence of AGR2-ER crosstalk was demonstrated by a reduction of ER at the protein level after transiently silencing AGR2. AGR2 knockdown in combination with fulvestrant or tamoxifen did not preclude the efficacy of the antiestrogens, but enhanced it. In addition, p-Src, implicated in tamoxifen resistance, was downregulated with AGR2 knockdown.
Conclusions: Transiently silencing AGR2 in ER-positive breast cancer cell lines inhibited cell growth and cell-cycle progression and induced cell death. Breast cancer drivers (ER and cyclin D1) as well as cancer-signaling nodes (pSrc, c-Myc, and survivin) were demonstrated to be downstream of AGR2. Collectively, the data presented support the utility of anti-AGR2 therapy in ER-positive breast cancers because of its impact on cancer-relevant pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Binding of anterior gradient 2 and estrogen receptor-α: Dual critical roles in enhancing fulvestrant resistance and IGF-1-induced tumorigenesis of breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2016 Jul 10;377(1):32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27063095
-
p53 status influences response to tamoxifen but not to fulvestrant in breast cancer cell lines.Int J Cancer. 2011 Apr 15;128(8):1813-21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25512. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20549698
-
Protein kinase D1 regulates ERα-positive breast cancer cell growth response to 17β-estradiol and contributes to poor prognosis in patients.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Dec;18(12):2536-52. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12322. Epub 2014 Oct 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25287328 Free PMC article.
-
The estrogen-regulated anterior gradient 2 (AGR2) protein in breast cancer: a potential drug target and biomarker.Breast Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 24;15(2):204. doi: 10.1186/bcr3408. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23635006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Killing the second messenger: targeting loss of cell cycle control in endocrine-resistant breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011 Jul 4;18(4):C19-24. doi: 10.1530/ERC-11-0112. Print 2011 Aug. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21613412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The secreted factor Ag1 missing in higher vertebrates regulates fins regeneration in Danio rerio.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 29;5:8123. doi: 10.1038/srep08123. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25630240 Free PMC article.
-
Association of increased primary breast tumor AGR2 with decreased disease-specific survival.Oncotarget. 2018 May 1;9(33):23114-23125. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25225. eCollection 2018 May 1. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29796176 Free PMC article.
-
AGR2: a secreted protein worthy of attention in diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 May 1;13:1195885. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1195885. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37197416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anterior gradient protein 2 (AGR2) is an independent prognostic factor in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma.Virchows Arch. 2012 Aug;461(2):109-16. doi: 10.1007/s00428-012-1273-4. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Virchows Arch. 2012. PMID: 22752467
-
Leveraging the Role of the Metastatic Associated Protein Anterior Gradient Homologue 2 in Unfolded Protein Degradation: A Novel Therapeutic Biomarker for Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 26;11(7):890. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070890. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31247903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2005, National Cancer Institute. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2005/
-
- Dubik D, Shiu RP. Mechanism of estrogen activation of c-myc oncogene expression. Oncogene. 1992;7:1587–94. - PubMed
-
- Altucci L, Addeo R, Cicatiello L, Dauvois S, Parker MG, Truss M, Beato M, Sica V, Bresciani F, Weisz A. 17beta-Estradiol induces cyclin D1 gene transcription, p36D1-p34cdk4 complex activation and p105Rb phosphorylation during mitogenic stimulation of G(1)-arrested human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 1996;12:2315–24. - PubMed
-
- Gillett C, Fantl V, Smith R, Fisher C, Bartek J, Dickson C, Barnes D, Peters G. Amplification and overexpression of cyclin D1 in breast cancer detected by immunohistochemical staining. Cancer Res. 1994;54:1812–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

