Analysis of cell cycle-related proteins in gastric intramucosal differentiated-type cancers based on mucin phenotypes: a novel hypothesis of early gastric carcinogenesis based on mucin phenotype
- PMID: 20525401
- PMCID: PMC2903504
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-55
Analysis of cell cycle-related proteins in gastric intramucosal differentiated-type cancers based on mucin phenotypes: a novel hypothesis of early gastric carcinogenesis based on mucin phenotype
Abstract
Background: Abnormalities of cell cycle regulators are common features in human cancers, and several of these factors are associated with the early development of gastric cancers. However, recent studies have shown that gastric cancer tumorigenesis was characterized by mucin expression. Thus, expression patterns of cell cycle-related proteins were investigated in the early phase of differentiated-type gastric cancers to ascertain any mechanistic relationships with mucin phenotypes.
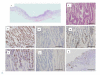
Methods: Immunostaining for Cyclins D1, A, E, and p21, p27, p53 and beta-catenin was used to examine impairments of the cell cycle in 190 gastric intramucosal differentiated-type cancers. Mucin phenotypes were determined by the expressions of MUC5AC, MUC6, MUC2 and CD10. A Ki-67 positive rate (PR) was also examined.
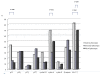
Results: Overexpressions of p53, cyclin D1 and cyclin A were significantly more frequent in a gastric phenotype than an intestinal phenotype. Cyclin A was overexpressed in a mixed phenotype compared with an intestinal phenotype, while p27 overexpression was more frequent in an intestinal phenotype than in a mixed phenotype. Reduction of p21 was a common feature of the gastric intramucosal differentiated-type cancers examined.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the levels of some cell cycle regulators appear to be associated with mucin phenotypes of early gastric differentiated-type cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of mucin, p53 protein and Ki-67 expressions in gastric differentiated-type intramucosal neoplastic lesions obtained from endoscopic mucosal resection samples: a proposal for a new classification of intramucosal neoplastic lesions based on nuclear atypia.Pathol Int. 2004 Jun;54(6):425-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2004.01643.x. Pathol Int. 2004. PMID: 15144402
-
Re-evaluation of mucin phenotypes of gastric minute well-differentiated-type adenocarcinomas using a series of HGM, MUC5AC, MUC6, M-GGMC, MUC2 and CD10 stains.Pathol Int. 2004 May;54(5):311-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2004.01625.x. Pathol Int. 2004. PMID: 15086835
-
Gastric mucin phenotype indicates aggressive biological behaviour in early differentiated gastric adenocarcinomas following endoscopic treatment.Diagn Pathol. 2021 Jul 13;16(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13000-021-01122-2. Diagn Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34256780 Free PMC article.
-
Three independent genetic profiles based on mucin expression in early differentiated-type gastric cancers--a new concept of genetic carcinogenesis of early differentiated-type adenocarcinomas.Mod Pathol. 2004 Oct;17(10):1223-34. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800170. Mod Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15154009
-
Loss of gastric gland mucin-specific O-glycan is associated with progression of differentiated-type adenocarcinoma of the stomach.Cancer Sci. 2014 Jan;105(1):126-33. doi: 10.1111/cas.12305. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24138592 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular profiling and comprehensive genome-wide analysis of somatic copy number alterations in gastric intramucosal neoplasias based on microsatellite status.Gastric Cancer. 2018 Sep;21(5):765-775. doi: 10.1007/s10120-018-0810-5. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Gastric Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29468422 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic differences stratified by PCR-based microsatellite analysis in gastric intramucosal neoplasia.Gastric Cancer. 2017 Mar;20(2):286-296. doi: 10.1007/s10120-016-0616-2. Epub 2016 May 28. Gastric Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27236438
-
Clinical significances of p27 in digestive tract cancers: a comprehensive analysis on immunohistochemistry staining, published literatures, microarray and RNA-seq data.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 23;9(15):12284-12303. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24316. eCollection 2018 Feb 23. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29552310 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of CD10 in tumor-associated fibroblast of cancerized or recurrent colorectal adenomas].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016 May 25;45(4):335-341. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2016.07.02. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016. PMID: 27868405 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Molecular Profiling Based on KRAS/BRAF Mutation, Methylation, and Microsatellite Statuses in Serrated Lesions.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 Oct;63(10):2626-2638. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5167-4. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29974407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ioachim E. Expression patterns of cyclins D1, E and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21waf1/cip1, p27kip1 in colorectal carcinoma: correlation with other cell cycle regulators (pRb, p53 and Ki-67 and PCNA) and clinicopathological features. Int J Clin Pract. 2008;62:1736–1743. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01105.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gamboa-Dominguez A, Seidl S, Reyes-Gutierrez E, Hermannstädter C, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Busch R, Höfler H, Fend F, Luber B. Prognostic significance of p21WAF1/CIP1, p27Kip1, p53 and E-cadherin expression in gastric cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60:756–761. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.038976. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Moundhri MS, Nirmala V, Al-Hadabi I, Al-Mawaly K, Burney I, Al-Nabhani M, Thomas V, Ganguly SS, Grant C. The prognostic significance of p53, p27 kip1, p21 waf1, HER-2/neu, and Ki67 proteins expression in gastric cancer: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 121 Arab patients. J Surg Oncol. 2005;91:243–252. doi: 10.1002/jso.20324. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

