Essential in vivo roles of the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2: embryonic/neonatal lethality of CLEC-2-deficient mice by blood/lymphatic misconnections and impaired thrombus formation of CLEC-2-deficient platelets
- PMID: 20525685
- PMCID: PMC2915686
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130575
Essential in vivo roles of the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2: embryonic/neonatal lethality of CLEC-2-deficient mice by blood/lymphatic misconnections and impaired thrombus formation of CLEC-2-deficient platelets
Abstract
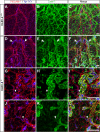
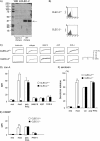
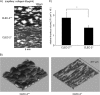
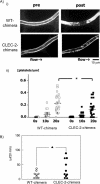
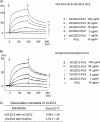
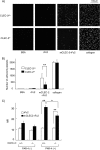
CLEC-2 has been described recently as playing crucial roles in thrombosis/hemostasis, tumor metastasis, and lymphangiogenesis. The snake venom rhodocytin is known as a strong platelet activator, and we have shown that this effect is mediated by CLEC-2 (Suzuki-Inoue, K., Fuller, G. L., García, A., Eble, J. A., Pöhlmann, S., Inoue, O., Gartner, T. K., Hughan, S. C., Pearce, A. C., Laing, G. D., Theakston, R. D., Schweighoffer, E., Zitzmann, N., Morita, T., Tybulewicz, V. L., Ozaki, Y., and Watson, S. P. (2006) Blood 107, 542-549). Podoplanin, which is expressed on the surface of tumor cells, is an endogenous ligand for CLEC-2 and facilitates tumor metastasis by inducing platelet aggregation. Mice deficient in podoplanin, which is also expressed on the surface of lymphatic endothelial cells, show abnormal patterns of lymphatic vessel formation. In this study, we report on the generation and phenotype of CLEC-2-deficient mice. These mice are lethal at the embryonic/neonatal stages associated with disorganized and blood-filled lymphatic vessels and severe edema. Moreover, by transplantation of fetal liver cells from Clec-2(-/-) or Clec-2(+/+) embryos, we were able to demonstrate that CLEC-2 is involved in thrombus stabilization in vitro and in vivo, possibly through homophilic interactions without apparent increase in bleeding tendency. We propose that CLEC-2 could be an ideal novel target protein for an anti-platelet drug, which inhibits pathological thrombus formation but not physiological hemostasis.
Figures



References
-
- Cambi A., Figdor C. G. (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 539–546 - PubMed
-
- Marshall A. S., Gordon S. (2004) Eur. J. Immunol. 34, 18–24 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki-Inoue K., Fuller G. L., García A., Eble J. A., Pöhlmann S., Inoue O., Gartner T. K., Hughan S. C., Pearce A. C., Laing G. D., Theakston R. D., Schweighoffer E., Zitzmann N., Morita T., Tybulewicz V. L., Ozaki Y., Watson S. P. (2006) Blood 107, 542–549 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki-Inoue K., Kato Y., Inoue O., Kaneko M. K., Mishima K., Yatomi Y., Yamazaki Y., Narimatsu H., Ozaki Y. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 25993–26001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

