Endothelial dysfunction and claudin 5 regulation during acrolein-induced lung injury
- PMID: 20525806
- PMCID: PMC3095921
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0391OC
Endothelial dysfunction and claudin 5 regulation during acrolein-induced lung injury
Abstract
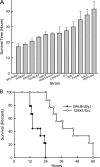
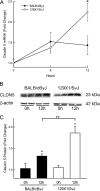
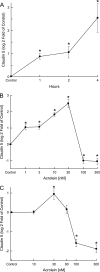
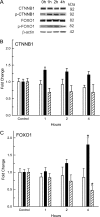
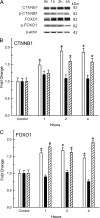
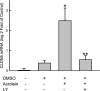
An integral membrane protein, Claudin 5 (CLDN5), is a critical component of endothelial tight junctions that control pericellular permeability. Breaching of endothelial barriers is a key event in the development of pulmonary edema during acute lung injury (ALI). A major irritant in smoke, acrolein can induce ALI possibly by altering CLDN5 expression. This study sought to determine the cell signaling mechanism controlling endothelial CLDN5 expression during ALI. To assess susceptibility, 12 mouse strains were exposed to acrolein (10 ppm, 24 h), and survival monitored. Histology, lavage protein, and CLDN5 transcripts were measured in the lung of the most sensitive and resistant strains. CLDN5 transcripts and phosphorylation status of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) and catenin (cadherin-associated protein) beta 1 (CTNNB1) proteins were determined in control and acrolein-treated human endothelial cells. Mean survival time (MST) varied more than 2-fold among strains with the susceptible (BALB/cByJ) and resistant (129X1/SvJ) strains (MST, 17.3 ± 1.9 h vs. 41.4 ± 5.1 h, respectively). Histological analysis revealed earlier perivascular enlargement in the BALB/cByJ than in 129X1/SvJ mouse lung. Lung CLDN5 transcript and protein increased more in the resistant strain than in the susceptible strain. In human endothelial cells, 30 nM acrolein increased CLDN5 transcripts and increased p-FOXO1 protein levels. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 diminished the acrolein-induced increased CLDN5 transcript. Acrolein (300 nM) decreased CLDN5 transcripts, which were accompanied by increased FOXO1 and CTNNB1. The phosphorylation status of these transcription factors was consistent with the observed CLDN5 alteration. Preservation of endothelial CLDN5 may be a novel clinical approach for ALI therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-muscle Mlck is required for β-catenin- and FoxO1-dependent downregulation of Cldn5 in IL-1β-mediated barrier dysfunction in brain endothelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2014 Apr 15;127(Pt 8):1840-53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.144550. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24522189 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Acrolein Exposure Induced Pulmonary Response in Seven Inbred Mouse Strains and Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells Cultured at Air-Liquid Interface.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 8;2020:3259723. doi: 10.1155/2020/3259723. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33110918 Free PMC article.
-
AKT2 maintains brain endothelial claudin-5 expression and selective activation of IR/AKT2/FOXO1-signaling reverses barrier dysfunction.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Feb;40(2):374-391. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18817512. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 30574832 Free PMC article.
-
Disheveled-1 Interacts with Claudin-5 and Contributes to Norrin-Induced Endothelial Barrier Restoration.Cells. 2023 Oct 4;12(19):2402. doi: 10.3390/cells12192402. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830616 Free PMC article.
-
CLDN5: From structure and regulation to roles in tumors and other diseases beyond CNS disorders.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Feb;200:107075. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107075. Epub 2024 Jan 14. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 38228255 Review.
Cited by
-
Claudins in lung diseases.Respir Res. 2011 May 27;12(1):70. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-70. Respir Res. 2011. PMID: 21619599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Haplotype association mapping of acute lung injury in mice implicates activin a receptor, type 1.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Jun 1;183(11):1499-509. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201006-0912OC. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21297076 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathology of pulmonary edema after injury in forensic autopsy cases.Int J Legal Med. 2012 Nov;126(6):875-82. doi: 10.1007/s00414-012-0758-7. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Int J Legal Med. 2012. PMID: 22885909
-
The Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Barrier Dysfunction in Respiratory Disease.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2021 Nov;13(6):850-862. doi: 10.4168/aair.2021.13.6.850. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34734504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Countermeasures against Pulmonary Threat Agents.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Jan 17;388(2):560-567. doi: 10.1124/jpet.123.001822. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 37863486 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Dejana E. Endothelial cell-cell junctions: happy together. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004;5:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg GA, Yang Y. Vasogenic edema due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral ischemia. Neurosurg Focus 2007;22:E4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

