AidH, an alpha/beta-hydrolase fold family member from an Ochrobactrum sp. strain, is a novel N-acylhomoserine lactonase
- PMID: 20525860
- PMCID: PMC2916461
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00477-10
AidH, an alpha/beta-hydrolase fold family member from an Ochrobactrum sp. strain, is a novel N-acylhomoserine lactonase
Abstract
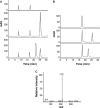
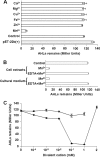
N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs) are signaling molecules in many quorum-sensing (QS) systems that regulate interactions between various pathogenic bacteria and their hosts. Quorum quenching by the enzymatic inactivation of AHLs holds great promise in preventing and treating infections, and several such enzymes have been reported. In this study, we report the characterization of a novel AHL-degrading protein from the soil bacterium Ochrobactrum sp. strain T63. This protein, termed AidH, shares no similarity with any of the known AHL degradases but is highly homologous with a hydrolytic enzyme from Ochrobactrum anthropi ATCC 49188 that contains the alpha/beta-hydrolase fold. By liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (MS) analysis, we demonstrate that AidH functions as an AHL-lactonase that hydrolyzes the ester bond of the homoserine lactone ring of AHLs. Mutational analyses indicate that the G-X-Nuc-X-G motif or the histidine residue conserved among alpha/beta-hydrolases is critical for the activity of AidH. Furthermore, the AHL-inactivating activity of AidH requires Mn(2+) but not several other tested divalent cations. We also showed that AidH significantly reduces biofilm formation by Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24 and the pathogenicity of Pectobacterium carotovorum, indicating that this enzyme is able to effectively quench QS-dependent functions in these bacteria by degrading AHLs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AidB, a Novel Thermostable N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from the Bacterium Bosea sp.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Nov 27;85(24):e02065-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02065-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31604771 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and characterization of bacteria from the potato rhizosphere degrading N-acyl-homoserine lactone.Can J Microbiol. 2006 Oct;52(10):1006-15. doi: 10.1139/w06-062. Can J Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17110970
-
High-resolution structures of AidH complexes provide insights into a novel catalytic mechanism for N-acyl homoserine lactonase.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Jan;69(Pt 1):82-91. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912042369. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23275166 Free PMC article.
-
MomL, a novel marine-derived N-acyl homoserine lactonase from Muricauda olearia.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Jan;81(2):774-82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02805-14. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25398866 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering acyl-homoserine lactone-interfering enzymes toward bacterial control.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 11;295(37):12993-13007. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.013531. Epub 2020 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32690609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Weapons to Fight Old Enemies: Novel Strategies for the (Bio)control of Bacterial Biofilms in the Food Industry.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 18;7:1641. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01641. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27803696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acinetobacter lactucae Strain QL-1, a Novel Quorum Quenching Candidate Against Bacterial Pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 17;10:2867. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02867. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31921047 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum quenching enzymes and their application in degrading signal molecules to block quorum sensing-dependent infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 26;14(9):17477-500. doi: 10.3390/ijms140917477. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24065091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing with special reference to use of quorum quenching bacteria in membrane biofouling control.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:162584. doi: 10.1155/2014/162584. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25147787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Subtleties and Contrasts of the LeuO Regulator in Salmonella Typhi: Implications in the Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2014 Dec 12;5:581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00581. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25566242 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burr, T., A. M. L. Barnard, M. J. Corbett, C. L. Pemberton, N. J. L. Simpson, and G. P. C. Salmond. 2006. Identification of the central quorum sensing regulator of virulence in the enteric phytopathogen, Erwinia carotovora: the VirR repressor. Mol. Microbiol. 59:113-125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

