High-dose atorvastatin causes a rapid sustained increase in human serum PCSK9 and disrupts its correlation with LDL cholesterol
- PMID: 20525997
- PMCID: PMC2918453
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M008144
High-dose atorvastatin causes a rapid sustained increase in human serum PCSK9 and disrupts its correlation with LDL cholesterol
Abstract
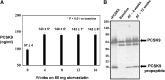
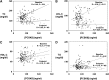
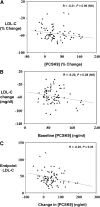
Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is a key regulator of serum LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) levels. PCSK9 is secreted by the liver into the plasma and binds the hepatic LDL receptor (LDLR), causing its subsequent degradation. We first demonstrated that a moderate dose of atorvastatin (40 mg) increases PCSK9 serum levels, suggesting why increasing statin doses may have diminished efficacy with regard to further LDL-C lowering. Since that initial observation, at least two other groups have reported statin-induced PCSK9 increases. To date, no analysis of the effect of high-dose atorvastatin (80 mg) on PCSK9 over time has been conducted. Therefore, we studied the time course of atorvastatin (80 mg) in human subjects. We measured PCSK9 and lipid levels during a 2-week lead-in baseline period and every 4 weeks thereafter for 16 weeks. We observed that atorvastatin (80 mg) caused a rapid 47% increase in serum PCSK9 at 4 weeks that was sustained throughout 16 weeks of dosing. Importantly, while PCSK9 levels were highly correlated with total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, and triglyceride (TG) levels at baseline, atorvastatin (80 mg) completely abolished all of these correlations. Together, these results further suggest an explanation for why increasing doses of statins fail to achieve proportional LDL-C lowering.
Figures

References
-
- Cao G., Qian Y. W., Kowala M. C., Konrad R. J. 2008. Further LDL cholesterol lowering through targeting PCSK9 for coronary artery disease. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets. 8: 238–243. - PubMed
-
- Seidah N. G. 2009. PCSK9 as a therapeutic target of dyslipidemia. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 13: 19–28. - PubMed
-
- Lambert G., Krempf M., Costet P. 2006. PCSK9: a promising therapeutic target for dyslipidemias. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 17: 79–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

