Palmitate induced IL-6 and MCP-1 expression in human bladder smooth muscle cells provides a link between diabetes and urinary tract infections
- PMID: 20526368
- PMCID: PMC2878332
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010882
Palmitate induced IL-6 and MCP-1 expression in human bladder smooth muscle cells provides a link between diabetes and urinary tract infections
Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infections (UTI) are more frequent in type-2 diabetes mellitus patients than in subjects with normal glucose metabolism. The mechanisms underlying this higher prevalence of UTI are unknown. However, cytokine levels are altered in diabetic patients and may thus contribute to the development of UTI. Increased levels of free fatty acids (FFA), as observed in obese patients, can induce IL-6 production in various cell types. Therefore we studied the effects of the free fatty acid palmitate and bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on interleukin-6 (IL-6) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) expression and secretion in cultured human bladder smooth muscle cells (hBSMC).
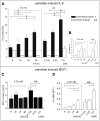
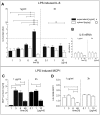
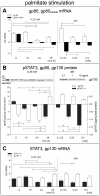
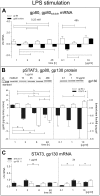
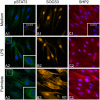
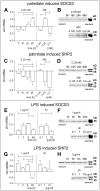
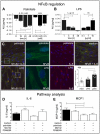
Methodology/principal findings: Biopsies were taken from patients undergoing cystectomy due to bladder cancer. Palmitate or LPS stimulated hBSMC were analysed for the production and secretion of the IL-6, gp80, gp80soluble, gp130, MCP-1, pSTAT3, SOCS3, NF-kappaB and SHP2 by quantitative PCR, ELISA, Western blotting, and confocal immunofluorescence. In signal transduction inhibition experiments we evaluated the involvement of NF-kappaB and MEK1 in IL-6 and MCP-1 regulation. Palmitate upregulates IL-6 mRNA expression and secretion via NF-kappaB dependent pathways in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. MCP-1 was moderately upregulated by palmitate but was strongly upregulated by LPS involving NF-kappaB and MEK1 dependent pathways. Soluble IL-6 receptor (gp80soluble) was downregulated by palmitate and LPS, while membrane-bound gp80 was moderately upregulated. LPS increased SOCS3 and SHP2, whereas palmitate only induced SOCS3. Secondary finding: most of the IL-6 is secreted.
Conclusions/significance: Bacterial infection (LPS) or metabolic alterations (palmitate) have distinct effects on IL-6 expression in hBSMC, (i) short term LPS induced autocrine JAK/STAT signaling and (ii) long-term endocrine regulation of IL-6 by palmitate. Induction of IL-6 in human bladder smooth muscle cells by fatty acids may represent a pathogenetic factor underlying the higher frequency and persistence of urinary tract infections in patients with metabolic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Free fatty acid palmitate impairs the vitality and function of cultured human bladder smooth muscle cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041026. Epub 2012 Jul 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22808290 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 on inflammatory cytokine expression and migration and proliferation of IL-6/IFN-γ-induced vascular smooth muscle cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Oct;33(5):615-622. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1168-x. Epub 2013 Oct 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24142708
-
Palmitate induced secretion of IL-6 and MCP-1 in orbital fibroblasts derived from patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Mol Vis. 2012;18:1467-77. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Mol Vis. 2012. PMID: 22736938 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitate induces interleukin-8 expression in human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells via Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway (TLR4/NF-κB-8).J Diabetes. 2014 Jan;6(1):33-41. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12073. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 23826669
-
SOCS3 promotor hypermethylation and STAT3-NF-κB interaction downregulate SOCS3 expression in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Mar 15;304(6):H776-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00570.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23335796 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Constitutive STAT3 phosphorylation contributes to skeletal muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes.Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):457-65. doi: 10.2337/db12-0337. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23043161 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of B7-1 (CD80) by RhuDex® reduces lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation in human atherosclerotic lesions.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 May 12;8:447-57. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S59594. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 24872677 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Demographic Factors and Blood Sugar Control on the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infections in Khorramabad in 2013.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2016 Feb 14;18(5):e21942. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.21942. eCollection 2016 May. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2016. PMID: 27478624 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency for costimulatory receptor 4-1BB protects against obesity-induced inflammation and metabolic disorders.Diabetes. 2011 Dec;60(12):3159-68. doi: 10.2337/db10-1805. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21998397 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and predictive biomarkers for bladder cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes presenting with haematuria.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2022 Sep;38(6):e3546. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3546. Epub 2022 May 22. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35578575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benfield T, Jensen JS, Nordestgaard BG. Influence of diabetes and hyperglycaemia on infectious disease hospitalisation and outcome. Diabetologia. 2007;50:549–554. - PubMed
-
- Stapleton A. Urinary tract infections in patients with diabetes. Am J Med. 2002;113(Suppl 1A):80S–84S. - PubMed
-
- Hoepelman AI, Meiland R, Geerlings SE. Pathogenesis and management of bacterial urinary tract infections in adult patients with diabetes mellitus. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2003;22(Suppl 2):35–43. - PubMed
-
- Harding GK, Zhanel GG, Nicolle LE, Cheang M. Antimicrobial treatment in diabetic women with asymptomatic bacteriuria. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1576–1583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

