Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor M344 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human THP-1 Leukemia Cells
- PMID: 20526416
- PMCID: PMC2880493
- DOI: 10.5099/aj090400352
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor M344 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human THP-1 Leukemia Cells
Abstract
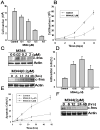
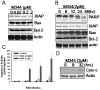
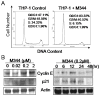
Histone acetylation plays an important role in the silencing and activation of genes involved in tumoregenesis. Trichostatin A, originally identified as an anti-fungal drug, is a potent inhibitor of histone deacetylase (HDAC) with potential anti-tumor activity. In this study, we investigated the effect of M344, an amide analogues of trichostatin A, on the growth and differentiation of THP-1 human leukemia cells. We showed that at low doses, (< 0.2 muM), M344 could inhibit the growth of THP-1 cells at G1 phase in vitro with low cytotoxic effect. Low dose of M344 exerted some differentiating effect on THP-1 cells as judged by the expression of c-fms proto-oncogene (M-CSF receptor) and appearance of adherent cells. Growth arrest induced by M344 is associated with increased levels of cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitor p21 and cyclin E, in agreement with G1 phase arrest. At higher doses (2 muM), M344 could induce THP-1 cells to undergo apoptosis, which was associated with the cleavage of PARP, cytochrome c release and activation of both caspases-8, -9, followed by the activation of caspase-3. In addition, M344 could increase the levels of pro-apoptotic protein Bax but decreased the levels of anti-apoptotic protein XIAP. M344 is a potent activator of NF-kappaB transcription factor. RT-PCR assay showed that the M344 could transiently increase IL-1 expression yet markedly decreased TNF-alpha expression. Our results show that M344 is a potent growth inhibitor and inducer of apoptosis in human leukemia cells and suggest potential therapeutic strategies of HDAC inhibitors for patients with leukemias.
Figures

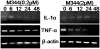
References
-
- Marmorstein R. Structural and chemical basis of histone acetylation. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:78–98. discussion 98–101, 163–9. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, et al. Transcription regulation by histone deacetylases. Novartis Found Symp. 2004;259:238–45. discussion 245–8, 285–8. - PubMed
-
- Kuo MH, Allis CD. Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. Bioessays. 1998;20(8):615–26. - PubMed
-
- Ito K, I, Adcock M. Histone acetylation and histone deacetylation. Mol Biotechnol. 2002;20(1):99–106. - PubMed
-
- Chambers AE, et al. Histone acetylation-mediated regulation of genes in leukaemic cells. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39(8):1165–75. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
