Early Intervention Approaches to Enhance the Peer-Related Social Competence of Young Children With Developmental Delays: A Historical Perspective
- PMID: 20526420
- PMCID: PMC2880512
- DOI: 10.1097/IYC.0b013e3181d22e14
Early Intervention Approaches to Enhance the Peer-Related Social Competence of Young Children With Developmental Delays: A Historical Perspective
Abstract
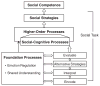
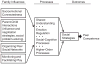
This article presents a framework for future research and program development designed to support children's peer-related social competence. Intervention research is examined within a historical perspective culminating with a discussion of contemporary translational approaches capable of integrating models of normative development, developmental models of risk and disability, and intervention science.
Figures

References
-
- Baker JK, Fenning RM, Crnic KA, Baker BL, Blacher J. Prediction of social skills in 6-year-old children with and without developmental delays: Contributions of early regulation and maternal scaffolding. American Journal on Mental Retardation. 2007;112:375–391. - PubMed
-
- Banich MT. Executive function: The search for an integrated account. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 2009;18:89–94.
-
- Brown WH, Conroy MA. Promoting peer-related social-communicative competence in preschool children. In: Goldstein H, Kaczmarek LA, English KM, editors. Promoting social communication: Children with developmental disabilities from birth to adolescence. Baltimore: Brookes; 2002. pp. 173–210.
-
- Brown WH, Odom SL, McConnell SR, Rathel JM. Peer interaction interventions for preschool children with developmental difficulties. In: Brown WH, Odom SL, McConnell SR, editors. Social competence of young children: Risk, disability, and intervention. 2. Baltimore: Brookes; 2008. pp. 141–163.
-
- Brownell CA. Convergent developments: Cognitive-developmental correlates of growth in infant/toddler peer skills. Child Development. 1986;57:275–286.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
