Factor structure of the acute stress disorder scale in a sample of Hurricane Katrina evacuees
- PMID: 20528054
- PMCID: PMC2883796
- DOI: 10.1037/a0018506
Factor structure of the acute stress disorder scale in a sample of Hurricane Katrina evacuees
Abstract
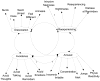
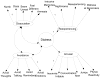
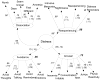
Acute stress disorder (ASD) is a poorly understood and controversial diagnosis (A. G. Harvey & R. A. Bryant, 2002). The present study used confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the factor structure of the most widely used self-report measure of ASD, the Acute Stress Disorder Scale (R. A. Bryant, M. L. Moulds, & R. M. Guthrie, 2000), in a sample of Hurricane Katrina evacuees relocated to a Red Cross emergency shelter in Austin, Texas. Results indicated that the proposed 4-factor structure did not fit the data well. However, an alternate 2-factor model did fit the data well. This model included a second-order Distress factor (onto which the Reexperiencing, Arousal, and Avoidance factors loaded strongly) that was positively correlated with the Dissociation factor. Implications for the ASD construct and its measurement are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Do religious habits and coping help in the immediate aftermath of a crisis? Relations with Hurricane Katrina evacuees' acute stress symptoms and functional impairment.Psychol Trauma. 2019 Sep;11(6):563-570. doi: 10.1037/tra0000426. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Psychol Trauma. 2019. PMID: 30570286
-
The structure of acute stress disorder among Chinese adults exposed to an earthquake: is dysphoric arousal a unique construct of acute posttraumatic responses?Scand J Psychol. 2012 Oct;53(5):430-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9450.2012.00965.x. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Scand J Psychol. 2012. PMID: 22882702
-
Different profiles of acute stress disorder differentially predict posttraumatic stress disorder in a large sample of female victims of sexual trauma.Psychol Assess. 2014 Dec;26(4):1155-61. doi: 10.1037/a0037272. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Psychol Assess. 2014. PMID: 24978131
-
A review of acute stress disorder in DSM-5.Depress Anxiety. 2011 Sep;28(9):802-17. doi: 10.1002/da.20737. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Depress Anxiety. 2011. PMID: 21910186 Review.
-
Acute stress disorder revisited.Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011;7:245-67. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104502. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011. PMID: 21275643 Review.
Cited by
-
Examining the Latent Structure of Acute Stress Disorder Symptoms in Filipino-Victims of a Flashflood Disaster.Community Ment Health J. 2015 Jul;51(5):613-20. doi: 10.1007/s10597-015-9826-z. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Community Ment Health J. 2015. PMID: 25575912
-
The latent structure of Acute Stress Disorder symptoms in trauma-exposed children and adolescents.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov;57(11):1308-1316. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12597. Epub 2016 Jul 30. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27472990 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to warfare and demoralization: acute stress symptoms and disengaged coping as a mediators.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2025 Dec;16(1):2449308. doi: 10.1080/20008066.2024.2449308. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2025. PMID: 39801397 Free PMC article.
-
Acute stress disorder, coping self-efficacy and subsequent psychological distress among nurses amid COVID-19.J Nurs Manag. 2020 Oct;28(7):1686-1695. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13124. Epub 2020 Aug 30. J Nurs Manag. 2020. PMID: 32767827 Free PMC article.
-
Association of posttraumatic stress disorder and depression with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality and hospitalization among Hurricane Katrina survivors with end-stage renal disease.Am J Public Health. 2013 Apr;103(4):e130-7. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2012.301146. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Am J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 23409901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 1974;19(6):716–723.
-
- American Red Cross. 2007 Annual Report. Accessed October. 2008. p. 2008. Available at: http://www.redcross.org/static/file_cont7590_lang0_3181.pdf.
-
- APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Aassociation; 2000. Text Revision.
-
- Arbuckle JL. Amos16.0 User’s Guide. Chicago, IL: SPSS Inc; 2007.
-
- Asmundson G, Stapleton J, Taylor S. Are avoidance and numbing distinct PTSD symptom clusters? Journal of Traumatic Stress. 2004;17:467–475. - PubMed

