The multifunctional SNM1 gene family: not just nucleases
- PMID: 20528238
- PMCID: PMC2904241
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.10.47
The multifunctional SNM1 gene family: not just nucleases
Abstract
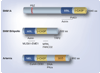
The archetypical member of the SNM1 gene family was discovered 30 years ago in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This small but ubiquitous gene family is characterized by metallo-beta-lactamase and beta-CASP domains, which together have been demonstrated to comprise a nuclease activity. Three mammalian members of this family, SNM1A, SNM1B/Apollo and Artemis, have been demonstrated to play surprisingly divergent roles in cellular metabolism. These pathways include variable (diversity) joining recombination, nonhomologous end-joining of double-strand breaks, DNA damage and mitotic cell cycle checkpoints, telomere maintenance and protein ubiquitination. Not all of these functions are consistent with a model in which these proteins act only as nucleases, and indicate that the SNM1 gene family encodes multifunctional products that can act in diverse biochemical pathways. In this article we discuss the various functions of SNM1A, SNM1B/Apollo and Artemis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and Function of SNM1 Family Nucleases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1414:1-26. doi: 10.1007/5584_2022_724. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 35708844 Review.
-
DNA cross-link repair protein SNM1A interacts with PIAS1 in nuclear focus formation.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;24(24):10733-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10733-10741.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15572677 Free PMC article.
-
The SNM1/Pso2 family of ICL repair nucleases: from yeast to man.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010 Jul;51(6):635-45. doi: 10.1002/em.20556. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2010. PMID: 20175117
-
The role of SNM1 family nucleases in etoposide-induced apoptosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jul 8;410(3):568-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.027. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21683065
-
New features on Pso2 protein family in DNA interstrand cross-link repair and in the maintenance of genomic integrity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Fungal Genet Biol. 2013 Nov;60:122-32. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Fungal Genet Biol. 2013. PMID: 24076078 Review.
Cited by
-
DCLRE1B as a novel prognostic biomarker associated with immune infiltration: a pancancer analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80603-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738287 Free PMC article.
-
CSB interacts with SNM1A and promotes DNA interstrand crosslink processing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(1):247-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1279. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25505141 Free PMC article.
-
The telomeric protein SNM1B/Apollo is required for normal cell proliferation and embryonic development.Aging Cell. 2010 Dec;9(6):1047-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00631.x. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Aging Cell. 2010. PMID: 20854421 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestrating the nucleases involved in DNA interstrand cross-link (ICL) repair.Cell Cycle. 2011 Dec 1;10(23):3999-4008. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.23.18385. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 22101340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Function of SNM1 Family Nucleases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1414:1-26. doi: 10.1007/5584_2022_724. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 35708844 Review.
References
-
-
Haase E, Riehl D, Mack M, Brendel M. Molecular cloning of SNM1, a yeast gene responsible for a specific step in the repair of cross-linked DNA. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1989;218(1):64–71.▪ Cloning of the founding member of the sensitivity to nitrogen mustard (SNM1) gene family in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
-
-
- Ruhland A, Kircher M, Wilborn F, Brendel M. A yeast mutant specifically sensitive to bifunctional alkylation. Mutat. Res. 1981;91(6):457–462. - PubMed
-
- Bonatto D, Revers LF, Brendel M, Henriques JA. The eukaryotic Pso2/Snm1/Artemis proteins and their function as genomic and cellular caretakers. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005;38(3):321–334. - PubMed
-
- Dominski Z. Nucleases of the metallo-β-lactamase family and their role in DNA and RNA metabolism. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007;42(2):67–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
