Ecological genomics: steps towards unraveling the genetic basis of inducible defenses in Daphnia
- PMID: 20529235
- PMCID: PMC2867779
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-51
Ecological genomics: steps towards unraveling the genetic basis of inducible defenses in Daphnia
Abstract
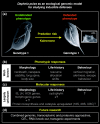
Little is known about the genetic mechanisms underlying inducible defenses. Recently, the genome of Daphnia pulex, a model organism for defense studies, has been sequenced. Building on the genome information, recent preliminary studies in BMC Developmental Biology and BMC Molecular Biology have assessed gene response profiles in Daphnia under predation pressure. We review the significance of the findings and highlight future research perspectives.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The water flea Daphnia--a 'new' model system for ecology and evolution?J Biol. 2010;9(2):21. doi: 10.1186/jbiol212. Epub 2010 Jan 13. J Biol. 2010. PMID: 20478012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How do consumers deal with stoichiometric constraints? Lessons from functional genomics using Daphnia pulex.Mol Ecol. 2011 Jun;20(11):2341-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05102.x. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Mol Ecol. 2011. PMID: 21521393
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis for Understanding Predator-Induced Polyphenism in the Water Flea Daphnia pulex.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 20;19(7):2110. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072110. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30036973 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological genomics in Daphnia: stress responses and environmental sex determination.Heredity (Edinb). 2008 Feb;100(2):184-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800999. Epub 2007 May 23. Heredity (Edinb). 2008. PMID: 17519967 Review.
-
wFleaBase: the Daphnia genome database.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Mar 7;6:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-45. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15752432 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genomic changes under rapid evolution: selection for parasitoid resistance.Proc Biol Sci. 2014 Feb 5;281(1779):20132303. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.2303. Print 2014 Mar 22. Proc Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24500162 Free PMC article.
-
Not just another genome.BMC Biol. 2011 Feb 4;9:8. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-9-8. BMC Biol. 2011. PMID: 21294909 Free PMC article.
-
Mesozoic fossils (>145 Mya) suggest the antiquity of the subgenera of Daphnia and their coevolution with chaoborid predators.BMC Evol Biol. 2011 May 19;11:129. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-129. BMC Evol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21595889 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient Endemic or Recent Invader? Phylogenetic Position and the Probable Origin of the Ccladoceran Diaphanosoma macedonicum (Diplostraca, Sididae) from the Ancient Lakes in the Balkans.Zool Stud. 2024 May 3;62:e9. doi: 10.6620/ZS.2024.63-09. eCollection 2024. Zool Stud. 2024. PMID: 39544525 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of Daphnia magna hints at molecular pathways involved in defensive plastic responses.BMC Genomics. 2014 Apr 24;15:306. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-306. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24762235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tollrian R, Harvell CD. The Ecology and Evolution of Inducible Defenses. Princeton University Press; 1999.
-
- Krueger DA, Dodson SI. Embryological induction and predation ecology in Daphnia pulex. Limnol Oceanogr. 1981;8:219–223. doi: 10.4319/lo.1981.26.2.0219. - DOI
-
- Stibor H, Luening J. Predator-induced phenotypic variation in the pattern of growth and reproduction in Daphnia hyalina (Crustacea, Cladocera) Funct Ecol. 1994;8:97–101. doi: 10.2307/2390117. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

