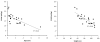Extravascular lung water index measurement in critically ill children does not correlate with a chest x-ray score of pulmonary edema
- PMID: 20529308
- PMCID: PMC2911751
- DOI: 10.1186/cc9054
Extravascular lung water index measurement in critically ill children does not correlate with a chest x-ray score of pulmonary edema
Erratum in
- Crit Care. 2010;14(4):430
Abstract
Introduction: Extravascular lung water index (EVLWI) can be measured at the bedside using the transpulmonary thermodilution technique (TPTD). The goal of this study was to compare EVLWI values with a chest x-ray score of pulmonary edema and markers of oxygenation in critically ill children.
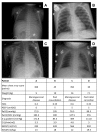
Methods: This was a prospective observational study in a pediatric intensive care unit of a university hospital. We included 27 critically ill children with an indication for advanced invasive hemodynamic monitoring. No specific interventions for the purpose of the study were carried out. Measurements included EVLWI and other relevant hemodynamic variables. Blood gas analysis, ventilator parameters, chest x-ray and TPTD measurements were obtained within a three-hour time frame. Two radiologists assessed the chest x-ray and determined a score for pulmonary edema.
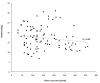
Results: A total of 103 measurements from 24 patients were eligible for final analysis. Mean age was two years (range: two months to eight years). Median cardiac index was 4.00 (range: 1.65 to 10.85) l/min/m2. Median EVLWI was 16 (range: 6 to 31) ml/kg. The weighted kappa between the chest x-ray scores of the two radiologists was 0.53. There was no significant correlation between EVLWI or chest x-ray score and the number of ventilator days, severity of illness or markers of oxygenation. There was no correlation between EVLWI and the chest x-ray score. EVLWI was significantly correlated with age and length (r2 of 0.47 and 0.67 respectively).
Conclusions: The extravascular lung water index in critically ill children does not correlate with a chest x-ray score of pulmonary edema, nor with markers of oxygenation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Assessing the quantity of pulmonary edema in critically ill children.Crit Care. 2010;14(4):189. doi: 10.1186/cc9199. Epub 2010 Aug 13. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 20804574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cecchetti C, Lubrano R, Cristaldi S, Stoppa F, Barbieri MA, Elli M, Masciangelo R, Perrotta D, Travasso E, Raggi C, Marano M, Pirozzi N. Relationship between global end-diastolic volume and cardiac output in critically ill infants and children. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:928–932. - PubMed
-
- Phillips CR, Chesnutt MS, Smith SM. Extravascular lung water in sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: Indexing with predicted body weight improves correlation with severity of illness and survival. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:69–73. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000295314.01232.BE. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources