Dorsal ruffle microdomains potentiate Met receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and down-regulation
- PMID: 20529867
- PMCID: PMC2915731
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.127985
Dorsal ruffle microdomains potentiate Met receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and down-regulation
Abstract
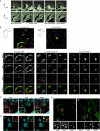
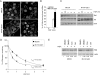
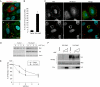
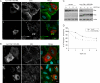
Dorsal ruffles are apical protrusions induced in response to many growth factors, yet their function is poorly understood. Here we report that downstream from the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), Met, dorsal ruffles function as both a localized signaling microdomain as well as a platform from which the Met RTK internalizes and traffics to a degradative compartment. In response to HGF, colonies of epithelial Madin-Darby canine kidney cells form dorsal ruffles for up to 20 min. Met is transcytosed from the basolateral membrane on Rab4 endosomes, to the apical surface where Met, as well as a Met substrate and scaffold protein, Gab1, localize to the dorsal ruffle membrane. This results in activation of downstream signaling proteins, as evidenced by localization of phospho-ERK1/2 to dorsal ruffles. As dorsal ruffles collapse, Met is internalized into EEA1- and Rab5-positive endosomes and is targeted for degradation through delivery to an Hrs-positive sorting compartment. Enhancing HGF-dependent dorsal ruffle formation, through overexpression of Gab1 or activated Pak1 kinase, promotes more efficient degradation of the Met RTK. Conversely, the ablation of dorsal ruffle formation, by pre-treatment with SITS (4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyabatostilbene-2',2-disulfonic acid) or expression of a Gab1 mutant, impairs Met degradation. Taken together, these data support a function for dorsal ruffles as a biologically relevant signaling microenvironment and a mechanism for Met receptor internalization and degradation.
Figures


References
-
- Jones M. C., Caswell P. T., Norman J. C. (2006) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 18, 549–557 - PubMed
-
- Sorkin A., Von Zastrow M. (2002) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 600–614 - PubMed
-
- Abella J. V., Park M. (2009) Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 296, 973–984 - PubMed
-
- Doherty G. J., McMahon H. T. (2009) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 857–902 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

