Estimating genome-wide IBD sharing from SNP data via an efficient hidden Markov model of LD with application to gene mapping
- PMID: 20529903
- PMCID: PMC2881389
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq204
Estimating genome-wide IBD sharing from SNP data via an efficient hidden Markov model of LD with application to gene mapping
Abstract
Motivation: Association analysis is the method of choice for studying complex multifactorial diseases. The premise of this method is that affected persons contain some common genomic regions with similar SNP alleles and such areas will be found in this analysis. An important disadvantage of GWA studies is that it does not distinguish between genomic areas that are inherited from a common ancestor [identical by descent (IBD)] and areas that are identical merely by state [identical by state (IBS)]. Clearly, areas that can be marked with higher probability as IBD and have the same correlation with the disease status of identical areas that are more probably only IBS, are better candidates to be causative, and yet this distinction is not encoded in standard association analysis.
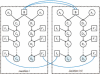
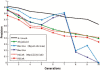
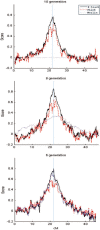
Results: We develop a factorial hidden Markov model-based algorithm for computing genome-wide IBD sharing. The algorithm accepts as input SNP data of measured individuals and estimates the probability of IBD at each locus for every pair of individuals. For two g-degree relatives, when g > or = 8, the computation yields a precision of IBD tagging of over 50% higher than previous methods for 95% recall. Our algorithm uses a first-order Markovian model for the linkage disequilibrium process and employs a reduction of the state space of the inheritance vector from being exponential in g to quadratic. The higher accuracy along with the reduced time complexity marks our method as a feasible means for IBD mapping in practical scenarios.
Availability: A software implementation, called IBDMAP, is freely available at http://bioinfo.cs.technion.ac.il/IBDmap.
Figures
References
-
- Abecasis GR, et al. Merlin-rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Bercovici S, Geiger D. Inferring ancestries efficiently in admixed populations with linkage disequilibrium. J. Comput. Biol. 2009;16:1141–1150. - PubMed
-
- Browning S, Browning B. On reducing the statespace of hidden markov models for the identity by descent process. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2002;62:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

