Using semantic web rules to reason on an ontology of pseudogenes
- PMID: 20529940
- PMCID: PMC2881358
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq173
Using semantic web rules to reason on an ontology of pseudogenes
Abstract
Motivation: Recent years have seen the development of a wide range of biomedical ontologies. Notable among these is Sequence Ontology (SO) which offers a rich hierarchy of terms and relationships that can be used to annotate genomic data. Well-designed formal ontologies allow data to be reasoned upon in a consistent and logically sound way and can lead to the discovery of new relationships. The Semantic Web Rules Language (SWRL) augments the capabilities of a reasoner by allowing the creation of conditional rules. To date, however, formal reasoning, especially the use of SWRL rules, has not been widely used in biomedicine.
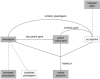
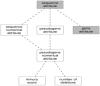
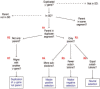
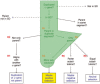
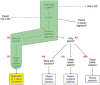
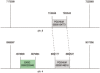
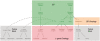
Results: We have built a knowledge base of human pseudogenes, extending the existing SO framework to incorporate additional attributes. In particular, we have defined the relationships between pseudogenes and segmental duplications. We then created a series of logical rules using SWRL to answer research questions and to annotate our pseudogenes appropriately. Finally, we were left with a knowledge base which could be queried to discover information about human pseudogene evolution.
Availability: The fully populated knowledge base described in this document is available for download from http://ontology.pseudogene.org. A SPARQL endpoint from which to query the dataset is also available at this location.
Figures

References
-
- Bailey JA, Eichler EE. Primate segmental duplications: crucibles of evolution, diversity and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:552–564. - PubMed
-
- Bechhofer S, Philip Lord RV. ISWC 2003. Berlin: Springer; 2003. Cooking the semantic web with the OWL API; pp. 659–675.
-
- Ding Z, Peng Y. Proceedings of the 37th Hawaii International Conference On System Sciences (HICSS-37) Big Island: IEEE.; 2004. A probabilistic extension to ontology language owl.
-
- Duplication,S. 2010. [last accessed date January 8, 2010]. Available at http://humanparalogy.gs.washington.edu/build36/build36.htm.

