Functional and physical interaction between the selenium-binding protein 1 (SBP1) and the glutathione peroxidase 1 selenoprotein
- PMID: 20530237
- PMCID: PMC2915633
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgq114
Functional and physical interaction between the selenium-binding protein 1 (SBP1) and the glutathione peroxidase 1 selenoprotein
Abstract
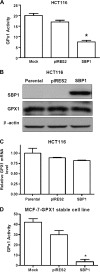
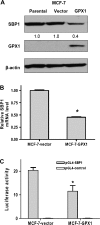
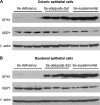
Selenium-binding protein (SBP) 1 is present in reduced levels in several cancer types as compared with normal tissues, and lower levels are associated with poor clinical prognosis. Another selenium-containing protein, glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1), has been associated with cancer risk and development. The interaction between these representatives of different classes of selenoproteins was investigated. Increasing SBP1 levels in either human colorectal or breast cancer cells by transfection of an expression construct resulted in the reduction of GPX1 enzyme activity. Increased expression of GPX1 in the same cell types resulted in the transcriptional and translational repression of SBP1, as evidenced by the reduction of SBP1 messenger RNA and protein and the inhibition of transcription measured using an SBP1 reporter construct. The opposing effects of SBP1 and GPX1 on each other were also observed when GPX1 was increased by supplementing the media of these tissue culture cells with selenium, and the effect of selenium on SBP1 was shown to be GPX1 dependent. Decreasing or increasing GPX1 levels in colonic epithelial cells of mice fed a selenium-deficient, -adequate or -supplemented diet resulted in the opposing effect on SBP1 levels. These data are explained in part by the demonstration that SBP1 and GPX1 form a physical association, as determined by coimmunoprecipitation and fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. The results presented establish an interaction between two distinct selenium-containing proteins that may enhance the understanding of the mechanisms by which selenium and selenoproteins affect carcinogenesis in humans.
Figures



References
-
- Behne D, et al. Mammalian selenium-containing proteins. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001;21:453–473. - PubMed
-
- Kryukov GV, et al. Characterization of mammalian selenoproteomes. Science. 2003;300:1439–1443. - PubMed
-
- Clark LC, et al. Effects of selenium supplementation for cancer prevention in patients with carcinoma of the skin. A randomized controlled trial. Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Study Group. JAMA. 1996;276:1957–1963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

