Occupational exposure to trichloroethylene is associated with a decline in lymphocyte subsets and soluble CD27 and CD30 markers
- PMID: 20530238
- PMCID: PMC2930801
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgq121
Occupational exposure to trichloroethylene is associated with a decline in lymphocyte subsets and soluble CD27 and CD30 markers
Abstract
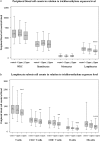
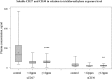
Occupational cohort and case-control studies suggest that trichloroethylene (TCE) exposure may be associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) but findings are not consistent. There is a need for mechanistic studies to evaluate the biologic plausibility of this association. We carried out a cross-sectional molecular epidemiology study of 80 healthy workers that used TCE and 96 comparable unexposed controls in Guangdong, China. Personal exposure measurements were taken over a three-week period before blood collection. Ninety-six percent of workers were exposed to TCE below the current US Occupational Safety and Health Administration Permissible Exposure Limit (100 p.p.m. 8 h time-weighted average), with a mean (SD) of 22.2 (36.0) p.p.m. The total lymphocyte count and each of the major lymphocyte subsets including CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, natural killer (NK) cells and B cells were significantly decreased among the TCE-exposed workers compared with controls (P < 0.05), with evidence of a dose-dependent decline. Further, there was a striking 61% decline in sCD27 plasma level and a 34% decline in sCD30 plasma level among TCE-exposed workers compared with controls. This is the first report that TCE exposure under the current Occupational Safety and Health Administration workplace standard is associated with a decline in all major lymphocyte subsets and sCD27 and sCD30, which play an important role in regulating cellular activity in subsets of T, B and NK cells and are associated with lymphocyte activation. Given that altered immunity is an established risk factor for NHL, these results add to the biologic plausibility that TCE is a possible lymphomagen.
Figures
References
-
- Gist GL, et al. Trichloroethylene—a review of the literature from a health effects perspective. Toxicol. Ind. Health. 1995;11:253–307. - PubMed
-
- IARC. Dry Cleaning, Some Chlorinated Solvents and Other Industrial Chemicals. Lyon, France: International Agency For Research on Cancer; 1995. Thesis/Dissertation. - PubMed
-
- Blossom SJ, et al. Activation and attenuation of apoptosis of CD4+ T cells following in vivo exposure to two common environmental toxicants, trichloroacetaldehyde hydrate and trichloroacetic acid. J. Autoimmun. 2004;23:211–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

