Multicenter survey on the outcome of transplantation of hematopoietic cells in patients with the complete form of DiGeorge anomaly
- PMID: 20530285
- PMCID: PMC4425440
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-275966
Multicenter survey on the outcome of transplantation of hematopoietic cells in patients with the complete form of DiGeorge anomaly
Abstract
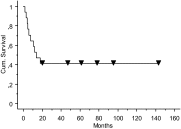
Seventeen patients transplanted with hematopoietic cells to correct severe T lymphocyte immunodeficiency resulting from complete DiGeorge anomaly were identified worldwide, and retrospective data were obtained using a questionnaire-based survey. Patients were treated at a median age of 5 months (range, 2-53 months) between 1995 and 2006. Bone marrow was used in 11 procedures in 9 cases: 6 from matched unrelated donors, 4 from human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical siblings, and one haploidentical parent with T-cell depletion. Unmobilized peripheral blood was used in 8 cases: 5 from HLA-identical siblings, one from a matched unrelated donor, one from an HLA-identical parent, and one unrelated matched cord blood. Conditioning was used in 5 patients and graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in 11 patients. Significant graft-versus-host disease occurred in 9 patients, becoming chronic in 3. Median length of follow-up was 13 months, with transplantation from HLA-matched sibling showing the best results. Median survival among deceased patients (10 patients) was 7 months after transplantation (range, 2-18 months). The overall survival rate was 41%, with a median follow-up of 5.8 years (range, 4-11.5 years). Among survivors, median CD3 and CD4 counts were 806 (range, 644-1224) and 348 (range, 225-782) cells/mm(3), respectively, CD4(+)/CD45RA(+) cells remained very low, whereas mitogen responses were normalized.
References
-
- Gosseye S, Golaire MC, Verellen G, Van Lierde M, Claus D. Association of bilateral renal agenesis and Di George syndrome in an infant of a diabetic mother. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1982;37(5):471–474. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Martinez-Frias ML, Graham JM., Jr Infants of diabetic mothers are at increased risk for the oculo-auriculo-vertebral sequence: a case-based and case-control approach. J Pediatr. 2002;141(5):611–617. - PubMed
-
- Oskarsdottir S, Persson C, Eriksson BO, Fasth A. Presenting phenotype in 100 children with the 22q11 deletion syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2005;164(3):146–153. - PubMed
-
- Markert ML, Alexieff MJ, Li J, et al. Complete DiGeorge syndrome: development of rash, lymphadenopathy, and oligoclonal T cells in 5 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113(4):734–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials