The GW/WG repeats of Drosophila GW182 function as effector motifs for miRNA-mediated repression
- PMID: 20530530
- PMCID: PMC2965232
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq501
The GW/WG repeats of Drosophila GW182 function as effector motifs for miRNA-mediated repression
Abstract
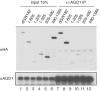
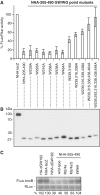
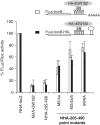
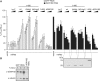
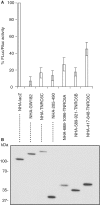
The control of messenger RNA (mRNA) function by micro RNAs (miRNAs) in animal cells requires the GW182 protein. GW182 is recruited to the miRNA repression complex via interaction with Argonaute protein, and functions downstream to repress protein synthesis. Interaction with Argonaute is mediated by GW/WG repeats, which are conserved in many Argonaute-binding proteins involved in RNA interference and miRNA silencing, from fission yeast to mammals. GW182 contains at least three effector domains that function to repress target mRNA. Here, we analyze the functions of the N-terminal GW182 domain in repression and Argonaute1 binding, using tethering and immunoprecipitation assays in Drosophila cultured cells. We demonstrate that its function in repression requires intact GW/WG repeats, but does not involve interaction with the Argonaute1 protein, and is independent of the mRNA polyadenylation status. These results demonstrate a novel role for the GW/WG repeats as effector motifs in miRNA-mediated repression.
Figures


References
-
- Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. 2008;132:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Chekulaeva M, Filipowicz W. Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2009;21:452–460. - PubMed
-
- Nilsen TW. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells. Trends Genet. 2007;23:243–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

