Targeting Hedgehog--a cancer stem cell pathway
- PMID: 20530699
- PMCID: PMC2888641
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2846
Targeting Hedgehog--a cancer stem cell pathway
Abstract
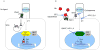
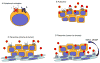
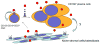
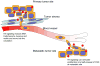
The Hedgehog (Hh) pathway has been implicated in a wide variety of human tumors, and early clinical trials with pathway antagonists have validated Hh signaling as a bona fide anticancer target. Despite these encouraging results, several issues surrounding the basic biology of the Hh pathway in human cancers remain unclear. These include the influence of specific oncogenic events on Hh signal transduction, the precise mode of Hh signaling (i.e., autocrine or paracrine) that occurs within human tumors, and the best means to inhibit aberrant pathway activity in the clinical setting. The cancer stem cell (CSC) hypothesis may explain a number of clinical phenomena, such as unchecked self-renewal and the development of metastatic disease, and to some extent, the Hh signaling pathway has been implicated in all of these processes. Therefore, Hh pathway inhibitors may also represent some of the first agents to formally examine the CSC hypothesis in the clinical setting. The diverse nature of Hh signaling in human cancers suggests that disease-specific factors must be carefully considered to identify the optimal use of novel pathway inhibitors.
(c) 2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
W. Matsui, commercial research grant, Merck; patent interest, Infinity Pharmaceuticals; consultant, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer.
Figures
References
-
- Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. 1980;287:795–801. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–87. - PubMed
-
- Varjosalo M, Taipale J. Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2454–72. - PubMed
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. In vivo analysis of quiescent adult neural stem cells responding to Sonic Hedgehog. Nature. 2005;437:894–7. - PubMed
-
- Watkins DN, Berman DM, Burkholder SG, Wang B, Beachy PA, Baylin SB. Hedgehog signalling within airway epithelial progenitors and in small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2003;422:313–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

