Disposition of cannabinoids in oral fluid after controlled around-the-clock oral THC administration
- PMID: 20530732
- PMCID: PMC3171507
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.141853
Disposition of cannabinoids in oral fluid after controlled around-the-clock oral THC administration
Abstract
Background: Oral fluid, a promising alternative matrix for drug monitoring in clinical and forensic investigations, offers noninvasive sample collection under direct observation. Cannabinoid distribution into oral fluid is complex and incompletely characterized due to the lack of controlled drug administration studies.
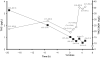
Methods: To characterize cannabinoid disposition in oral fluid, we administered around-the-clock oral Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (Marinol) doses to 10 participants with current daily cannabis use. We obtained oral fluid samples (n=440) by use of Quantisal collection devices before, during, and after 37 20-mg THC doses over 9 days. Samples were extracted with multiple elution solvents from a single SPE column and analyzed by 2-dimensional GC-MS with electron-impact ionization for THC, 11-hydroxy-THC (11-OH-THC), cannabidiol, and cannabinol and negative chemical ionization for 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC (THCCOOH). Linear ranges were 0.5-50 microg/L, with the exception of cannabinol (1-50 microg/L) and THCCOOH (7.5-500 ng/L).
Results: THCCOOH was the most prevalent analyte in 432 samples (98.2%), with concentrations up to 1117.9 ng/L. In contrast, 11-OH-THC was not identified in any sample; cannabidiol and cannabinol were quantified in 3 and 8 samples, respectively, with maximum concentrations of 2.1 and 13 microg/L. THC was present in only 20.7% of samples, with highest concentrations near admission (median 4.2 microg/L, range 0.6-481.9) from previously self-administered smoked cannabis.
Conclusions: Measurement of THCCOOH in OF not only identifies cannabis exposure, but also minimizes the possibility of passive inhalation. THCCOOH may be a better analyte for detection of cannabis use.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cannabinoids and metabolites in expectorated oral fluid after 8 days of controlled around-the-clock oral THC administration.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 Aug;401(2):599-607. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5066-4. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21637933 Free PMC article.
-
Oral fluid cannabinoids in chronic, daily Cannabis smokers during sustained, monitored abstinence.Clin Chem. 2011 Aug;57(8):1127-36. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2011.164822. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Clin Chem. 2011. PMID: 21677094
-
Oral fluid and plasma cannabinoid ratios after around-the-clock controlled oral Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol administration.Clin Chem. 2011 Nov;57(11):1597-606. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2011.169490. Epub 2011 Aug 29. Clin Chem. 2011. PMID: 21875944 Free PMC article.
-
Current knowledge on cannabinoids in oral fluid.Drug Test Anal. 2014 Jan-Feb;6(1-2):88-111. doi: 10.1002/dta.1514. Epub 2013 Aug 25. Drug Test Anal. 2014. PMID: 23983217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpretation of oral fluid tests for drugs of abuse.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Mar;1098:51-103. doi: 10.1196/annals.1384.037. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17332074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoids and metabolites in expectorated oral fluid after 8 days of controlled around-the-clock oral THC administration.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 Aug;401(2):599-607. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5066-4. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21637933 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous quantification of Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol, 11-nor-9-carboxy-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol in oral fluid by microflow-liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Jul 5;1297:123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.04.071. Epub 2013 Apr 30. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 23726246 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of 11-nor-9-carboxy-δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in human oral fluid by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Ther Drug Monit. 2014 Apr;36(2):225-33. doi: 10.1097/01.ftd.0000443071.30662.01. Ther Drug Monit. 2014. PMID: 24622724 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cannabinoid disposition in oral fluid after controlled cannabis smoking in frequent and occasional smokers.Drug Test Anal. 2014 Oct;6(10):1002-10. doi: 10.1002/dta.1632. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Drug Test Anal. 2014. PMID: 24652685 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of oral fluid in antidoping testing.Clin Chem. 2014 Feb;60(2):307-22. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.209676. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Clin Chem. 2014. PMID: 24153253 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verstraete AG. Oral fluid testing for driving under the influence of drugs: history, recent progress and remaining challenges. Forensic Sci Int. 2005;150:143–50. - PubMed
-
- Halldin MM, Widman M, Bahr CV, Lindgren JE, Martin BR. Identification of in vitro metabolites of delta-tetrahydrocannabinol formed by human livers. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982;10:297–301. - PubMed
-
- Huestis MA. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the plant cannabinoids, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and cannabinol. In: Pertwee RG, editor. Cannabinoids. vol. 168. Springer; New York: 2005. pp. 657–90. Handbook of experimental pharmacology. - PubMed
-
- Harvey DJ, Paton WDM. Metabolism of the cannabinoids. Rev Biochem Toxicol. 1986;6:221–64.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous