Inhibition of radiation-induced DNA repair and prosurvival pathways contributes to vorinostat-mediated radiosensitization of pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 20531243
- PMCID: PMC2955787
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181dd63e1
Inhibition of radiation-induced DNA repair and prosurvival pathways contributes to vorinostat-mediated radiosensitization of pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
Objective: The intrinsic radioresistance of pancreatic cancer (PaCa) is caused by multiple oncogenic signaling pathways. In contrast to combining radiation therapy (RT) with targeted therapeutic agent(s) whose blockade can be circumvented by redundant signaling pathways, we evaluated the combination of RT with a broad-spectrum histone deacetylase inhibitor, vorinostat.
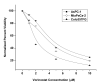
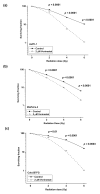
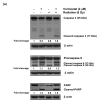
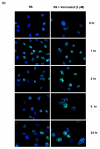
Methods: Radiosensitization by vorinostat was analyzed using clonogenic survival assays. Apoptosis was evaluated using flow cytometry and immunoblotting. DNA repair was evaluated using immunofluorescence assessment of histone 2AX phosphorylation and immunoblotting for DNA repair proteins. Prosurvival pathway proteins were measured by immunoblotting and electrophoretic mobility shift assays.
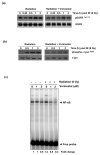
Results: Vorinostat significantly sensitized PaCa cells to radiation, but vorinostat-induced apoptosis did not contribute significantly to the observed radiosensitization. However, vorinostat inhibited DNA damage repair by targeting key DNA repair proteins and also abrogated prosurvival pathways responsible for PaCa aggressiveness and radioresistance. Specifically, the constitutively overexpressed epidermal growth factor receptor and nuclear factor κB pathways were shown to be induced by radiation and inhibited by vorinostat.
Conclusions: Vorinostat augments the antitumor effects of RT by abrogating radioresistance responses of PaCa cells mediated by prosurvival and DNA repair pathways and promises to be a clinically relevant adjunct to RT for treatment of PaCa.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances the response of human tumor cells to ionizing radiation through prolongation of gamma-H2AX foci.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Aug;5(8):1967-74. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0022. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16928817
-
Molecular sequelae of histone deacetylase inhibition in human retinoblastoma cell lines: clinical implications.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Sep;50(9):4072-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3517. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19387079
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor induces DNA damage, which normal but not transformed cells can repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 17;107(33):14639-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008522107. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20679231 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced signaling pathways that promote cancer cell survival (review).Int J Oncol. 2014 Nov;45(5):1813-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2614. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25174607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Signaling Pathways That Promote Radioresistance of Cancer Cells.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;12(3):656. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030656. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New targeted therapies in pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 28;21(20):6127-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6127. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26034349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vorinostat as a radiosensitizer for brain metastasis: a phase I clinical trial.J Neurooncol. 2014 Jun;118(2):313-319. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1433-2. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Neurooncol. 2014. PMID: 24728831 Clinical Trial.
-
Stereotactic MR-Guided Radiotherapy for Pancreatic Tumors: Dosimetric Benefit of Adaptation and First Clinical Results in a Prospective Registry Study.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 9;12:842402. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.842402. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35356227 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Implications of Nanoparticle-Enhanced Radiotherapy and Brachytherapy: Z-Effect and Tumor Hypoxia.Metabolites. 2022 Oct 5;12(10):943. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100943. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36295845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological determinants of radioresistance and their remediation in pancreatic cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Aug;1868(1):69-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28249796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maheshwari V, Moser AJ. Current management of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;2(8):356–364. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59(4):225–249. - PubMed
-
- Schneider G, Siveke JT, Eckel F, et al. Pancreatic cancer: basic and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology. 2005;128(6):1606–1625. - PubMed
-
- Krishnan S, Rana V, Janjan NA, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with unresectable locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma treated with chemoradiation. Cancer. 2006;107(11):2589–2596. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, van de Velde H, Karasek P, et al. Phase III trial of gemcitabine plus tipifarnib compared with gemcitabine plus placebo in advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(8):1430–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

