A mosaic mouse model of astrocytoma identifies alphavbeta8 integrin as a negative regulator of tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 20531304
- PMCID: PMC3037767
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.199
A mosaic mouse model of astrocytoma identifies alphavbeta8 integrin as a negative regulator of tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
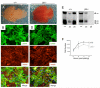
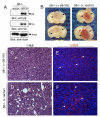
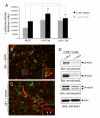
Angiogenesis involves a complex set of cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions that coordinately promote and inhibit blood vessel growth and sprouting. Although many factors that promote angiogenesis have been characterized, the identities and mechanisms of action of endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis remain unclear. Furthermore, little is known about how cancer cells selectively circumvent the actions of these inhibitors to promote pathological angiogenesis, a requisite event for tumor progression. Using mosaic mouse models of the malignant brain cancer, astrocytoma, we report that tumor cells induce pathological angiogenesis by suppressing expression of the ECM protein receptor alphavbeta8 integrin. Diminished integrin expression in astrocytoma cells leads to reduced activation of latent TGFbetas, resulting in impaired TGFbeta receptor signaling in tumor-associated endothelial cells. These data reveal that astrocytoma cells manipulate their angiogenic balance by selectively suppressing alphavbeta8 integrin expression and function. Finally, these results show that an adhesion and signaling axis normally involved in developmental brain angiogenesis is pathologically exploited in adult brain tumors.
Figures





References
-
- Abe M, Harpel JG, Metz CN, Nunes I, Loskutoff DJ, Rifkin DB. An assay for transforming growth factor-beta using cells transfected with a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter-luciferase construct. Anal Biochem. 1994;216:276–84. - PubMed
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–78. - PubMed
-
- Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:269–77. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006a;444:756–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

