Constitutive and chemokine-dependent internalization and recycling of CXCR7 in breast cancer cells to degrade chemokine ligands
- PMID: 20531309
- PMCID: PMC3164491
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.212
Constitutive and chemokine-dependent internalization and recycling of CXCR7 in breast cancer cells to degrade chemokine ligands
Abstract
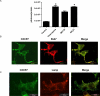
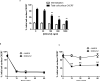
CXCR7 is a receptor for chemokines including CXCL12 (stromal-derived factor-1), a molecule that promotes tumor growth and metastasis in breast cancer and other malignancies. Building on the recent observation that CXCR7 sequesters CXCL12, we investigated mechanisms for CXCR7-dependent uptake of chemokines. Breast cancer cells expressing CXCR7 accumulated chemokines CXCL12 and CXC11 present at concentrations <1 ng/ml, unlike cells expressing CXCR4. CXCR7-dependent accumulation of chemokines was reduced by inhibitors of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. After CXCR7-mediated internalization, CXCL12 trafficked to lysosomes and was degraded, although levels of CXCR7 remained stable. CXCR7 reduced CXCL12 in the extracellular space, limiting the amounts of chemokine available to acutely stimulate signaling through CXCR4. CXCR7 constitutively internalized and recycled to the cell membrane even in the absence of ligand, and addition of chemokines did not significantly enhance receptor internalization. Chemokines at concentrations less than the Kd values for ligand-receptor binding did not alter levels of CXCR7 at the cell surface. Higher concentrations of chemokine ligands reduced the total cell surface expression of CXCR7 without affecting receptor internalization, indicating that receptor recycling was inhibited. CXCR7-dependent uptake of chemokines and receptor trafficking were regulated by beta-arrestin 2. These studies establish mechanisms through which CXCR7 regulates the availability of chemokine ligands in the extracellular space.
Figures






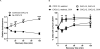
Similar articles
-
Imaging ligand-dependent activation of CXCR7.Neoplasia. 2009 Oct;11(10):1022-35. doi: 10.1593/neo.09724. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19794961 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine CXCL12 activates dual CXCR4 and CXCR7-mediated signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells.J Transl Med. 2012 Apr 2;10:68. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-68. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22472349 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR7 controls competition for recruitment of β-arrestin 2 in cells expressing both CXCR4 and CXCR7.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 4;9(6):e98328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098328. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24896823 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine receptor trio: CXCR3, CXCR4 and CXCR7 crosstalk via CXCL11 and CXCL12.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Feb;24(1):41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 16. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 22989616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Target in Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7371. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147371. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298991 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic platform for chemotaxis in gradients formed by CXCL12 source-sink cells.Integr Biol (Camb). 2010 Nov;2(11-12):680-6. doi: 10.1039/c0ib00041h. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Integr Biol (Camb). 2010. PMID: 20871938 Free PMC article.
-
C-X-C motif chemokine 12/C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 signaling regulates breast cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the tumor microenvironment.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 May 29;16(3):R54. doi: 10.1186/bcr3665. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24886617 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenging of CXCL12 by CXCR7 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of CXCR4-positive breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2012 Nov 8;31(45):4750-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.633. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22266857 Free PMC article.
-
Higher plasma CXCL12 levels predict incident myocardial infarction and death in chronic kidney disease: findings from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study.Eur Heart J. 2014 Aug 14;35(31):2115-22. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht481. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Eur Heart J. 2014. PMID: 24306482 Free PMC article.
-
The Signaling Duo CXCL12 and CXCR4: Chemokine Fuel for Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 21;12(10):3071. doi: 10.3390/cancers12103071. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33096815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allinen M, R B, Cai L, Brennan C, Lahti-Domerci J, Huang H, et al. Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:17–32. - PubMed
-
- Atanackovic D, Cao Y, Kim J, Brandl S, Thorn I, Faltz C, et al. The local cytokine and chemokine milieu within malignant effusions. Tumour Biol. 2008;29:93–104. - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, Chow K, Harriague J, Moepps B, et al. The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:35760–35766. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. - PubMed
-
- Boldajipour B, Mahabaleshwar S, Kardash E, Reichman-Fried M, Blaser H, Minina S, et al. Control of chemokine-guided cell migration by ligand sequestration. Cell. 2008;132:463–473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

