PLK2 phosphorylation is critical for CPAP function in procentriole formation during the centrosome cycle
- PMID: 20531387
- PMCID: PMC2910268
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.118
PLK2 phosphorylation is critical for CPAP function in procentriole formation during the centrosome cycle
Abstract
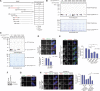
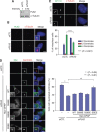
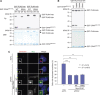
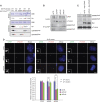
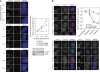
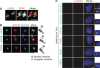
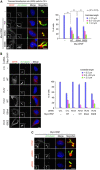
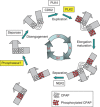
Control of centrosome duplication is tightly linked with the progression of the cell cycle. Recent studies suggest that the fundamental process of centriole duplication is evolutionally conserved. Here, we identified centrosomal P4.1-associated protein (CPAP), a human homologue of SAS-4, as a substrate of PLK2 whose activity oscillates during the cell cycle. PLK2 phosphorylates the S589 and S595 residues of CPAP in vitro and in vivo. This phosphorylation is critical for procentriole formation during the centrosome cycle. PLK4 also phosphorylates S595 of CPAP, but PLK4 phosphorylation is not a critical step in the PLK4 function in procentriole assembly. CPAP is phosphorylated in a cell cycle stage-specific manner, so that its phosphorylation increases at the G1/S transition phase and decreases during the exit of mitosis. Phosphorylated CPAP is preferentially located at the procentriole. Furthermore, overexpression of a phospho-resistant CPAP mutant resulted in the failure to form elongated centrioles. On the basis of these results, we propose that phosphorylated CPAP is involved in procentriole assembly, possibly for centriole elongation. This work demonstrates an example of how procentriole formation is linked to the progression of the cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Azimzadeh J, Bornens M (2007) Structure and duplication of the centrosome. J Cell Sci 120 (Pt 13): 2139–2142 - PubMed
-
- Bettencourt-Dias M, Glover DM (2007) Centrosome biogenesis and function: centrosomics brings new understanding. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 451–463 - PubMed
-
- Bettencourt-Dias M, Rodrigues-Martins A, Carpenter L, Riparbelli M, Lehmann L, Gatt MK, Carmo N, Balloux F, Callaini G, Glover DM (2005) SAK/PLK4 is required for centriole duplication and flagella development. Curr Biol 15: 2199–2207 - PubMed
-
- Bond J, Roberts E, Springell K, Lizarraga SB, Scott S, Higgins J, Hampshire DJ, Morrison EE, Leal GF, Silva EO, Costa SM, Baralle D, Raponi M, Karbani G, Rashid Y, Jafri H, Bennett C, Corry P, Walsh CA, Woods CG (2005) A centrosomal mechanism involving CDK5RAP2 and CENPJ controls brain size. Nat Genet 37: 353–355 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Indjeian VB, McManus M, Wang L, Dynlacht BD (2002) CP110, a cell cycle-dependent CDK substrate, regulates centrosome duplication in human cells. Dev Cell 3: 339–350 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

