Dis3-like 1: a novel exoribonuclease associated with the human exosome
- PMID: 20531389
- PMCID: PMC2910272
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.122
Dis3-like 1: a novel exoribonuclease associated with the human exosome
Abstract
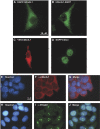
The exosome is an exoribonuclease complex involved in the degradation and maturation of a wide variety of RNAs. The nine-subunit core of the eukaryotic exosome is catalytically inactive and may have an architectural function and mediate substrate binding. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the associated Dis3 and Rrp6 provide the exoribonucleolytic activity. The human exosome-associated Rrp6 counterpart contributes to its activity, whereas the human Dis3 protein is not detectably associated with the exosome. Here, a proteomic analysis of immunoaffinity-purified human exosome complexes identified a novel exosome-associated exoribonuclease, human Dis3-like exonuclease 1 (hDis3L1), which was confirmed to associate with the exosome core by co-immunoprecipitation. In contrast to the nuclear localization of Dis3, hDis3L1 exclusively localized to the cytoplasm. The hDis3L1 isolated from transfected cells degraded RNA in an exoribonucleolytic manner, and its RNB domain seemed to mediate this activity. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of hDis3L1 in HeLa cells resulted in elevated levels of poly(A)-tailed 28S rRNA degradation intermediates, indicating the involvement of hDis3L1 in cytoplasmic RNA decay. Taken together, these data indicate that hDis3L1 is a novel exosome-associated exoribonuclease in the cytoplasm of human cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



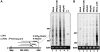
Comment in
-
Twins take the job.EMBO J. 2010 Jul 21;29(14):2260-1. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.148. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20648048 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Amblar M, Arraiano CM (2005) A single mutation in Escherichia coli ribonuclease II inactivates the enzyme without affecting RNA binding. FEBS J 272: 363–374 - PubMed
-
- Bonneau F, Basquin J, Ebert J, Lorentzen E, Conti E (2009) The yeast exosome functions as a macromolecular cage to channel RNA substrates for degradation. Cell 139: 547–559 - PubMed
-
- Brouwer R, Allmang C, Raijmakers R, van AY, Vree Egberts W, Petfalski E, van Venrooij WJ, Tollervey D, Pruijn GJ (2001a) Three novel components of the human exosome. J Biol Chem 276: 6177–6184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

