Chemical combinations elucidate pathway interactions and regulation relevant to Hepatitis C replication
- PMID: 20531405
- PMCID: PMC2913396
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2010.32
Chemical combinations elucidate pathway interactions and regulation relevant to Hepatitis C replication
Abstract
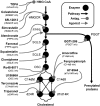
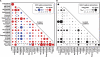
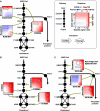
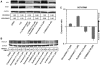
The search for effective Hepatitis C antiviral therapies has recently focused on host sterol metabolism and protein prenylation pathways that indirectly affect viral replication. However, inhibition of the sterol pathway with statin drugs has not yielded consistent results in patients. Here, we present a combination chemical genetic study to explore how the sterol and protein prenylation pathways work together to affect hepatitis C viral replication in a replicon assay. In addition to finding novel targets affecting viral replication, our data suggest that the viral replication is strongly affected by sterol pathway regulation. There is a marked transition from antagonistic to synergistic antiviral effects as the combination targets shift downstream along the sterol pathway. We also show how pathway regulation frustrates potential hepatitis C therapies based on the sterol pathway, and reveal novel synergies that selectively inhibit hepatitis C replication over host toxicity. In particular, combinations targeting the downstream sterol pathway enzymes produced robust and selective synergistic inhibition of hepatitis C replication. Our findings show how combination chemical genetics can reveal critical pathway connections relevant to viral replication, and can identify potential treatments with an increased therapeutic window.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic inhibition of intracellular hepatitis C virus replication by combination of ribavirin and interferon- alpha.J Infect Dis. 2004 Apr 1;189(7):1129-39. doi: 10.1086/382595. Epub 2004 Mar 16. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15031779
-
Discovery and characterization of substituted diphenyl heterocyclic compounds as potent and selective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Apr;52(4):1419-29. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00525-07. Epub 2008 Jan 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18227176 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism of host-based statin resistance in hepatitis C virus replicon containing cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Aug 1;96(3):190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26070251
-
Replication of the hepatitis C virus in cell culture.Antiviral Res. 2003 Oct;60(2):91-102. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2003.08.016. Antiviral Res. 2003. PMID: 14638404 Review.
-
A Hepatitis C virus-host interaction involved in viral replication: toward the identification of antiviral targets.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2010 Sep;63(5):307-11. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20858994 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic suppression of dengue virus replication using a combination of nucleoside analogs and nucleoside synthesis inhibitors.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Apr;59(4):2086-93. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04779-14. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25624323 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple cationic amphiphiles induce a Niemann-Pick C phenotype and inhibit Ebola virus entry and infection.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056265. Epub 2013 Feb 18. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23441171 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between sucrose and folate modulates auxin signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jul;162(3):1552-65. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.215095. Epub 2013 May 20. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23690535 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cellular squalene synthase, an enzyme essential for cholesterol biosynthesis, is a potential antiviral strategy against hepatitis C virus.J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(4):2220-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03385-14. Epub 2014 Dec 3. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25473062 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic Differences and Synergistic Antiviral Effects Between Type I and Type III Interferon Signaling Indicate Pathway Independence.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 Sep;35(9):734-47. doi: 10.1089/jir.2015.0008. Epub 2015 May 4. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015. PMID: 25938799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amemiya F, Maekawa S, Itakura Y, Kanayama A, Matsui A, Takano S, Yamaguchi T, Itakura J, Kitamura T, Inoue T, Sakamoto M, Yamauchi K, Okada S, Yamashita A, Sakamoto N, Itoh M, Enomoto N (2008) Targeting lipid metabolism in the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 197: 361–370 - PubMed
-
- Bader T, Fazili J, Madhoun M, Aston C, Hughes D, Rizvi S, Seres K, Hasan M (2008) Fluvastatin inhibits hepatitis C replication in humans. Am J Gastroenterol 103: 1383–1389 - PubMed
-
- Berkhout TA, Simon HM, Patel DD, Bentzen C, Niesor E, Jackson B, Suckling KE (1996) The novel cholesterol-lowering drug SR-12813 inhibits cholesterol synthesis via an increased degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J Biol Chem 271: 14376–14382 - PubMed
-
- Blight KJ, Kolykhalov AA, Rice CM (2000) Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290: 1972–1974 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

