Combined contrast-enhanced ultrasound and rt-PA treatment is safe and improves impaired microcirculation after reperfusion of middle cerebral artery occlusion
- PMID: 20531462
- PMCID: PMC3023400
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.82
Combined contrast-enhanced ultrasound and rt-PA treatment is safe and improves impaired microcirculation after reperfusion of middle cerebral artery occlusion
Erratum in
- J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Jul;31(7):1660
Abstract
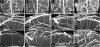
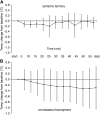
In monitoring of recanalization and in sonothrombolysis, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) is applied in extended time protocols. As extended use may increase the probability of unwanted effects, careful safety evaluation is required. We investigated the safety profile and beneficial effects of CEUS in a reperfusion model. Wistar rats were subjected to filament occlusion of the right middle cerebral artery (MCA). Reperfusion was established after 90 minutes, followed by recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) treatment and randomization to additional CEUS (contrast agent: SonoVue; 60 minutes). Blinded outcome evaluation consisted of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), neurologic assessment, and histology and, in separate experiments, quantitative 3D nano-computed tomography (CT) angiography (900 nm(3) voxel size). Nano-CT revealed severely compromised microcirculation in untreated animals after MCA reperfusion. The rt-PA partially improved hemispheric perfusion. Impairment was completely reversed in animals receiving rt-PA and CEUS. This combination was more effective than treatment with either CEUS without rt-PA or rt-PA and ultrasound or ultrasound alone. In MRI experiments, CEUS and rt-PA treatment resulted in a significantly reduced ischemic lesion volume and edema formation. No unwanted effects were detected on MRI, histology, and intracranial temperature assessment. This study shows that CEUS and rt-PA is safe in the situation of reperfusion and displays beneficial effects on the level of the microvasculature.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of MRI-based thrombolysis for patients with middle cerebral artery occlusion<or=3 h and 3-6 h.Neurol India. 2009 Jul-Aug;57(4):426-33. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.55615. Neurol India. 2009. PMID: 19770543 Clinical Trial.
-
Tirofiban combined with rt-PA intraarterial thrombolysis improves the recanalization rate of acute middle cerebral artery occlusion in rabbits.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(9):2888-2895. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14991. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29771445
-
Magnetic resonance angiography of thromboembolic stroke in rats: indicator of recanalization probability and tissue survival after recombinant tissue plasminogen activator treatment.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002 Jun;22(6):652-62. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200206000-00003. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002. PMID: 12045663
-
[Prospects of thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke].Brain Nerve. 2009 Sep;61(9):1003-12. Brain Nerve. 2009. PMID: 19803399 Review. Japanese.
-
Safety of urgent STA-MCA anastomosis after intravenous rt-PA treatment: a report of five cases and literature review.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018 Sep;160(9):1721-1727. doi: 10.1007/s00701-018-3576-y. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018. PMID: 29869110 Review.
Cited by
-
Sonothrombolysis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;880:339-62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22536-4_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26486347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine as a strategy to fight thrombotic diseases.Future Sci OA. 2015 Nov 1;1(4):FSO46. doi: 10.4155/fso.15.46. eCollection 2015 Nov. Future Sci OA. 2015. PMID: 28031907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-inflammatory mediators and apoptosis correlate to rt-PA response in a novel mouse model of thromboembolic stroke.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 20;9(1):e85849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085849. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465746 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Importance of Temporal Bone Features for the Efficacy of Contrast-Enhanced Sonothrombolysis: a Retrospective Analysis of the NOR-SASS Trial.Transl Stroke Res. 2018 Aug;9(4):333-339. doi: 10.1007/s12975-017-0583-x. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Transl Stroke Res. 2018. PMID: 29119369
-
Treatment of microvascular micro-embolization using microbubbles and long-tone-burst ultrasound: an in vivo study.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015 Feb;41(2):456-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2014.09.033. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25542487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexandrov AV, Molina CA, Grotta JC, Garami Z, Ford SR, Alvarez-Sabin J, Montaner J, Saqqur M, Demchuk AM, Moye LA, Hill MD, Wojner AW. Ultrasound-enhanced systemic thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2170–2178. - PubMed
-
- Allendoerfer J, Goertler M, von Reutern GM. Prognostic relevance of ultra-early Doppler sonography in acute ischaemic stroke: a prospective multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:835–840. - PubMed
-
- Daffertshofer M, Gass A, Ringleb P, Sitzer M, Sliwka U, Els T, Sedlaczek O, Koroshetz WJ, Hennerici MG. Transcranial low-frequency ultrasound-mediated thrombolysis in brain ischemia: increased risk of hemorrhage with combined ultrasound and tissue plasminogen activator: results of a phase II clinical trial. Stroke. 2005;36:1441–1446. - PubMed
-
- Dawson DA, Ruetzler CA, Hallenbeck JM. Temporal impairment of microcirculatory perfusion following focal cerebral ischemia in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Brain Res. 1997;749:200–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

