Glial glucokinase expression in adult and post-natal development of the hypothalamic region
- PMID: 20531973
- PMCID: PMC2881537
- DOI: 10.1042/AN20090059
Glial glucokinase expression in adult and post-natal development of the hypothalamic region
Abstract
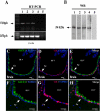
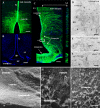
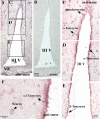
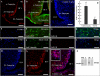
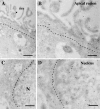
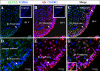
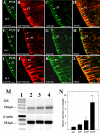
It has recently been proposed that hypothalamic glial cells sense glucose levels and release lactate as a signal to activate adjacent neurons. GK (glucokinase), the hexokinase involved in glucose sensing in pancreatic beta-cells, is also expressed in the hypothalamus. However, it has not been clearly determined if glial and/or neuronal cells express this protein. Interestingly, tanycytes, the glia that cover the ventricular walls of the hypothalamus, are in contact with CSF (cerebrospinal fluid), the capillaries of the arcuate nucleus and adjacent neurons; this would be expected for a system that can detect and communicate changes in glucose concentration. Here, we demonstrated by Western-blot analysis, QRT-PCR [quantitative RT-PCR (reverse transcription-PCR)] and in situ hybridization that GK is expressed in tanycytes. Confocal microscopy and immuno-ultrastructural analysis revealed that GK is localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm of beta1-tanycytes. Furthermore, GK expression increased in these cells during the second week of post-natal development. Based on this evidence, we propose that tanycytes mediate, at least in part, the mechanism by which the hypothalamus detects changes in glucose concentrations.
Keywords: CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; DIG, digoxigenin; DTT, dithiothreitol; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; GK, glucokinase; GKRP, GK regulatory protein; GLUT2, glucose transporter 2; RT–PCR, reverse transcription–PCR; TFIIB, transcription factor IIB; arcuate nucleus; brain; glia; glucokinase; glucosensing; tanycyte.
Figures
References
-
- Akmayev IG, Popov AP. Morphological aspects of the hypothalamic–hypophyseal system. VII. The tanycytes: their relation to the hypophyseal adrenocorticotrophic function. An ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1977;180:263–282. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez E, Roncero I, Chowen JA, Vazquez P, Blazquez E. Evidence that glucokinase regulatory protein is expressed and interacts with glucokinase in rat brain. J Neurochem. 2002;80:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Bady I, Marty N, Dallaporta M, Emery M, Gyger J, Tarussio D, Foretz M, Thorens B. Evidence from glut2-null mice that glucose is a critical physiological regulator of feeding. Diabetes. 2006;55:988–995. - PubMed
-
- Bali D, Svetlanov A, Lee HW, Fusco-DeMane D, Leiser M, Li B, Barzilai N, Surana M, Hou H, Fleischer N, DePinho R, Rossetti L, Efrat S. Animal model for maturity-onset diabetes of the young generated by disruption of the mouse glucokinase gene. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:21464–21467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

