Plasma concentrations of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate in critically ill children on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support
- PMID: 20532176
- PMCID: PMC2880602
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010938
Plasma concentrations of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate in critically ill children on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support
Abstract
Introduction: To evaluate the effect of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support on pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate (OC) in children.
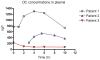
Methodology: Steady state 0-12 hour pharmacokinetic sampling was performed in new influenza A (H1N1) infected children treated with oseltamivir while on ECMO support. Cmax, Cmin and AUC(0-12 h) were calculated. The age-specific oseltamivir dosage was doubled to counter expected decreased plasma drug concentrations due to increased volume of distribution on ECMO support.
Principal findings: Three patients were enrolled aged 15, 6 and 14 years in this pharmacokinetic case series. For two children the OC plasma concentrations were higher than those found in children and adults not on ECMO. These increased plasma concentrations related to the increased oseltamivir dosage and decreased kidney function. In one patient suboptimal plasma concentrations coincided with a decreased gastric motility.
Conclusion: Oseltamivir pharmacokinetics do not appear to be significantly influenced by ECMO support. Caution is required in case of nasogastric administration and decreased gastric motility. Due to the limited number of (paediatric) patients available further multicenter studies are warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 76. http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_11_27a/en/index.html. 2009 [cited 28-11-2009]
-
- Dominguez-Cherit G, Lapinsky SE, Macias AE, Pinto R, Espinosa-Perez L, et al. Critically Ill patients with 2009 influenza A(H1N1) in Mexico. JAMA. 2009;302:1880–1887. - PubMed
-
- Davies A, Jones D, Bailey M, Beca J, Bellomo R, et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for 2009 Influenza A(H1N1) Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. JAMA. 2009;302:1888–1895. - PubMed
-
- Libster R, Bugna J, Coviello S, Hijano DR, Dunaiewsky M, et al. Pediatric hospitalizations associated with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Argentina. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:45–55. - PubMed
-
- Buck ML. Pharmacokinetic changes during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: implications for drug therapy of neonates. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42:403–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

