Prevalence and clinical significance of HIV drug resistance mutations by ultra-deep sequencing in antiretroviral-naïve subjects in the CASTLE study
- PMID: 20532178
- PMCID: PMC2880604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010952
Prevalence and clinical significance of HIV drug resistance mutations by ultra-deep sequencing in antiretroviral-naïve subjects in the CASTLE study
Abstract
Background: CASTLE compared the efficacy of atazanavir/ritonavir with lopinavir/ritonavir, each in combination with tenofovir-emtricitabine in ARV-naïve subjects from 5 continents.
Objectives: Determine the baseline rate and clinical significance of TDR mutations using ultra-deep sequencing (UDS) in ARV-naïve subjects in CASTLE.
Methods: A case control study was performed on baseline samples for all 53 subjects with virologic failures (VF) at Week 48 and 95 subjects with virologic successes (VS) randomly selected and matched by CD4 count and viral load. UDS was performed using 454 Life Sciences/Roche technology.
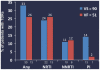
Results: Of 148 samples, 141 had successful UDS (86 subtype B, 55 non-B subtypes). Overall, 30.5% of subjects had a TDR mutation at baseline; 15.6% only had TDR(s) at <20% of the viral population. There was no difference in the rate of TDRs by B (30.2%) or non-B subtypes (30.9%). VF (51) and VS (90) had similar rates of any TDRs (25.5% vs. 33.3%), NNRTI TDRs (11.1% vs.11.8%) and NRTI TDRs (24.4% vs. 25.5%). Of 9 (6.4%) subjects with M184V/I (7 at <20% levels), 6 experienced VF. 16 (11.3%) subjects had multiple TAMs, and 7 experienced VF. 3 (2.1%) subjects had both multiple TAMs+M184V, and all experienced VF. Of 14 (9.9%) subjects with PI TDRs (11 at <20% levels): only 1 experienced virologic failure. The majority of PI TDRs were found in isolation (e.g. 46I) at <20% levels, and had low resistance algorithm scores.
Conclusion: Among a representative sample of ARV-naïve subjects in CASTLE, TDR mutations were common (30.5%); B and non-B subtypes had similar rates of TDRs. Subjects with multiple PI TDRs were infrequent. Overall, TDRs did not affect virologic response for subjects on a boosted PI by week 48; however, a small subset of subjects with extensive NRTI backbone TDR patterns experienced virologic failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kozal MJ, Shah N, Shen N, Yang R, Fucini R, et al. Extensive polymorphisms observed in HIV-1 clade B protease gene using high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat Med. 1996;2(7):753–759. - PubMed
-
- Stenman J, Lintula S, Rissanen O, Finne P, Hedstrom J, et al. Quantitative detection of low-copy-number mRNAs differing at single nucleotide positions. BioTechniques. 2003;34(1):172–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

