Epithelial p38alpha controls immune cell recruitment in the colonic mucosa
- PMID: 20532209
- PMCID: PMC2880565
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000934
Epithelial p38alpha controls immune cell recruitment in the colonic mucosa
Abstract
Intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) compose the first barrier against microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract. Although the NF-kappaB pathway in IECs was recently shown to be essential for epithelial integrity and intestinal immune homeostasis, the roles of other inflammatory signaling pathways in immune responses in IECs are still largely unknown. Here we show that p38alpha in IECs is critical for chemokine expression, subsequent immune cell recruitment into the intestinal mucosa, and clearance of the infected pathogen. Mice with p38alpha deletion in IECs suffer from a sustained bacterial burden after inoculation with Citrobacter rodentium. These animals are normal in epithelial integrity and immune cell function, but fail to recruit CD4(+) T cells into colonic mucosal lesions. The expression of chemokines in IECs is impaired, which appears to be responsible for the impaired T cell recruitment. Thus, p38alpha in IECs contributes to the host immune responses against enteric bacteria by the recruitment of immune cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
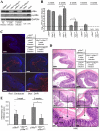

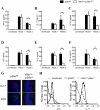
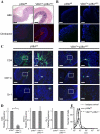
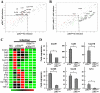

Similar articles
-
Activation of p38α in T cells regulates the intestinal host defense against attaching and effacing bacterial infections.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 1;191(5):2764-2770. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300908. Epub 2013 Aug 5. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23918973 Free PMC article.
-
Card9 mediates intestinal epithelial cell restitution, T-helper 17 responses, and control of bacterial infection in mice.Gastroenterology. 2013 Sep;145(3):591-601.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.05.047. Epub 2013 May 31. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23732773 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hypoxic exposure on immune responses of intestinal mucosa to Citrobacter colitis in mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110477. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110477. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32768962
-
Intestinal epithelium-specific MyD88 signaling impacts host susceptibility to infectious colitis by promoting protective goblet cell and antimicrobial responses.Infect Immun. 2014 Sep;82(9):3753-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02045-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24958710 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial Cells as a Transmitter of Signals From Commensal Bacteria and Host Immune Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 28;10:2057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02057. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Participation of the p38 pathway in Drosophila host defense against pathogenic bacteria and fungi.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 30;107(48):20774-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009223107. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21076039 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Specific Regulation of p38α-Mediated Inflammation in Con A-Induced Acute Liver Damage.J Immunol. 2015 May 15;194(10):4759-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402954. Epub 2015 Apr 17. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25888643 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of a Synbiotic against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Murine Infection Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Apr 22;60(5):3041-50. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02928-15. Print 2016 May. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 26953197 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL9 contributes to antimicrobial protection of the gut during citrobacter rodentium infection independent of chemokine-receptor signaling.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Feb 2;11(2):e1004648. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004648. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25643352 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of host signaling in the inflammatory response by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence proteins.Cell Mol Immunol. 2017 Mar;14(3):237-244. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2016.52. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27796284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HL. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:123–140. - PubMed
-
- Mead PS, Griffin PM. Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1998;352:1207–1212. - PubMed
-
- Borenshtein D, McBee ME, Schauer DB. Utility of the Citrobacter rodentium infection model in laboratory mice. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2008;24:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Eckmann L. Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease: lessons from enteric infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1072:28–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

