A Staphylococcus aureus small RNA is required for bacterial virulence and regulates the expression of an immune-evasion molecule
- PMID: 20532214
- PMCID: PMC2880579
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000927
A Staphylococcus aureus small RNA is required for bacterial virulence and regulates the expression of an immune-evasion molecule
Abstract
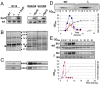
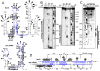
Staphylococcus aureus, a pathogen responsible for hospital and community-acquired infections, expresses many virulence factors under the control of numerous regulatory systems. Here we show that one of the small pathogenicity island RNAs, named SprD, contributes significantly to causing disease in an animal model of infection. We have identified one of the targets of SprD and our in vivo data demonstrate that SprD negatively regulates the expression of the Sbi immune-evasion molecule, impairing both the adaptive and innate host immune responses. SprD interacts with the 5' part of the sbi mRNA and structural mapping of SprD, its mRNA target, and the 'SprD-mRNA' duplex, in combination with mutational analysis, reveals the molecular details of the regulation. It demonstrates that the accessible SprD central region interacts with the sbi mRNA translational start site. We show by toeprint experiments that SprD prevents translation initiation of sbi mRNA by an antisense mechanism. SprD is a small regulatory RNA required for S. aureus pathogenicity with an identified function, although the mechanism of virulence control by the RNA is yet to be elucidated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dual RNA regulatory control of a Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(8):4847-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku119. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24510101 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA genes expressed from Staphylococcus aureus genomic and pathogenicity islands with specific expression among pathogenic strains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 4;102(40):14249-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503838102. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16183745 Free PMC article.
-
A non-coding RNA promotes bacterial persistence and decreases virulence by regulating a regulator in Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Mar 20;10(3):e1003979. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003979. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24651379 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII and Its Regulon Link Quorum Sensing, Stress Responses, Metabolic Adaptation, and Regulation of Virulence Gene Expression.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016 Sep 8;70:299-316. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095708. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27482744 Review.
-
Current knowledge on regulatory RNAs and their machineries in Staphylococcus aureus.RNA Biol. 2012 Apr;9(4):402-13. doi: 10.4161/rna.20103. Epub 2012 Apr 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22546940 Review.
Cited by
-
Contrasting silencing mechanisms of the same target mRNA by two regulatory RNAs in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Mar 16;46(5):2600-2612. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1287. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29294085 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of teg49 small RNA in the 5' upstream transcriptional region of sarA to virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 2014 Oct;82(10):4369-79. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02002-14. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25092913 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory RNAs in Virulence and Host-Microbe Interactions.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 Jul;6(4):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0002-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0002-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 30003867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA and its potential role in Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis.RNA Biol. 2012 Apr;9(4):427-36. doi: 10.4161/rna.20105. Epub 2012 Apr 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22546938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mobile genetic element SCCmec-encoded psm-mec RNA suppresses translation of agrA and attenuates MRSA virulence.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003269. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003269. Epub 2013 Apr 4. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23592990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520–532. - PubMed
-
- Moks T, et al. Staphylococcal protein A consists of five IgG-binding domains. Eur J Biochem. 1986;156:637–643. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Jacobsson K, Vasi J, Lindberg M, Frykberg L. A second IgG-binding protein in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology. 1998;145:985–991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

