Candidate genes for non-diabetic ESRD in African Americans: a genome-wide association study using pooled DNA
- PMID: 20532800
- PMCID: PMC3144421
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-010-0842-3
Candidate genes for non-diabetic ESRD in African Americans: a genome-wide association study using pooled DNA
Abstract
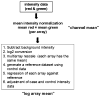
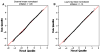
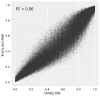
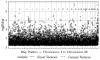
African Americans have increased susceptibility to non-diabetic (non-DM) forms of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and extensive evidence supports a genetic contribution. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) using pooled DNA was performed in 1,000 African Americans to detect associated genes. DNA from 500 non-DM ESRD cases and 500 non-nephropathy controls was quantified using gel electrophoresis and spectrophotometric analysis and pools of 50 case and 50 control DNA samples were created. DNA pools were genotyped in duplicate on the Illumina HumanHap550-Duo BeadChip. Normalization methods were developed and applied to array intensity values to reduce inter-array variance. Allele frequencies were calculated from normalized channel intensities and compared between case and control pools. Three SNPs had p values of <1.0E-6: rs4462445 (ch 13), rs4821469 (ch 22) and rs8077346 (ch 17). After normalization, top scoring SNPs (n = 65) were genotyped individually in 464 of the original cases and 478 of the controls, with replication in 336 non-DM ESRD cases and 363 non-nephropathy controls. Sixteen SNPs were associated with non-DM ESRD (p < 7.7E-4, Bonferroni corrected). Twelve of these SNPs are in or near the MYH9 gene. The four non-MYH9 SNPs that were associated with non-DM ESRD in the pooled samples were not associated in the replication set. Five SNPs that were modestly associated in the pooled samples were more strongly associated in the replication and/or combined samples. This is the first GWAS for non-DM ESRD in African Americans using pooled DNA. We demonstrate strong association between non-DM ESRD in African Americans with MYH9, and have identified additional candidate loci.
Figures
References
-
- Appel LJ, Wright JT, Jr, Greene T, Kusek JW, Lewis JB, Wang X, Lipkowitz MS, Norris KC, Bakris GL, Rahman M, Contreras G, Rostand SG, Kopple JD, Gabbai FB, Schulman GI, Gassman JJ, Charleston J, Agodoa LY. Long-term effects of renin-angiotensin system-blocking therapy and a low blood pressure goal on progression of hypertensive chronic kidney disease in African Americans. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:832–839. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chou JW, Paules RS, Bushel PR. Systematic variation normalization in microarray data to get gene expression comparison unbiased. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2005;3:225–241. - PubMed
-
- Dusel JA, Burdon KP, Hicks PJ, Hawkins GA, Bowden DW, Freedman BI. Identification of podocin (NPHS2) gene mutations in African Americans with nondiabetic end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2005;68:256–262. - PubMed
-
- Freedman BI, Langefeld CD, Rich SS, Valis CJ, Sale MM, Williams AH, Brown WM, Beck SR, Hicks PJ, Bowden DW. A genome scan for ESRD in black families enriched for nondiabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:2719–2727. - PubMed
-
- Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Rich SS, Valis CJ, Sale MM, Hicks PJ, Langefeld CD. A genome scan for all-cause end-stage renal disease in African Americans. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:712–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

