Differential HMG-CoA lyase expression in human tissues provides clues about 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria
- PMID: 20532825
- PMCID: PMC2903694
- DOI: 10.1007/s10545-010-9097-3
Differential HMG-CoA lyase expression in human tissues provides clues about 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria
Abstract
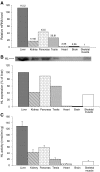
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria is a rare human autosomal recessive disorder caused by deficiency of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA lyase (HL). This mitochondrial enzyme catalyzes the common final step of leucine degradation and ketogenesis. Acute symptoms include vomiting, seizures and lethargy, accompanied by metabolic acidosis and hypoketotic hypoglycaemia. Such organs as the liver, brain, pancreas, and heart can also be involved. However, the pathophysiology of this disease is only partially understood. We measured mRNA levels, protein expression and enzyme activity of human HMG-CoA lyase from liver, kidney, pancreas, testis, heart, skeletal muscle, and brain. Surprisingly, the pancreas is, after the liver, the tissue with most HL activity. However, in heart and adult brain, HL activity was not detected in the mitochondrial fraction. These findings contribute to our understanding of the enzyme function and the consequences of its deficiency and suggest the need for assessment of pancreatic damage in these patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric aciduria and recurrent Reye-like syndrome].Rev Neurol. 1998 Jun;26(154):911-4. Rev Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9658458 Spanish.
-
GC/MS analysis of urine in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1992 Apr;34(2):157-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1992.tb00943.x. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1992. PMID: 1377861
-
More Than One HMG-CoA Lyase: The Classical Mitochondrial Enzyme Plus the Peroxisomal and the Cytosolic Ones.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 4;20(24):6124. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246124. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31817290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E37X is a common HMGCL mutation in Portuguese patients with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaric CoA lyase deficiency.Mol Genet Metab. 2004 Aug;82(4):334-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.06.003. Mol Genet Metab. 2004. PMID: 15308132
-
[3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaraciduria (case report of a female Turkish sisters with 3-hydroxy-3- methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A lyase deficiency].Klin Padiatr. 2000 May-Jun;212(3):113-6. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-10043. Klin Padiatr. 2000. PMID: 10916782 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Primary Metabolite Responses to Oxidative Stress in Early-Senescing and Paraquat Resistant Arabidopsis thaliana rcd1 (Radical-Induced Cell Death1).Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 28;11:194. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00194. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32180786 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel HMG-CoA lyase enzyme with a dual location in endoplasmic reticulum and cytosol.J Lipid Res. 2012 Oct;53(10):2046-2056. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M025700. Epub 2012 Jul 30. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22847177 Free PMC article.
-
CardioNet: a human metabolic network suited for the study of cardiomyocyte metabolism.BMC Syst Biol. 2012 Aug 29;6:114. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-6-114. BMC Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22929619 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of splice variants of the genes encoding human mitochondrial HMG-CoA lyase and HMG-CoA synthase, the main enzymes of the ketogenesis pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Apr;39(4):4777-85. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1270-8. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21952825
-
Environmental Enteric Dysfunction is Associated with Carnitine Deficiency and Altered Fatty Acid Oxidation.EBioMedicine. 2017 Mar;17:57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.01.026. Epub 2017 Jan 18. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28122695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashmarina LI, Rusnak N, Miziorko HM, et al. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase is present in mouse and human liver peroxisomes. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:31929–31932. - PubMed
-
- Bachhawat BK, Robinson WG, Coon MJ. The enzymatic cleavage of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A to acetoacetate and acetyl coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1955;216:727–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

