ABCB1/MDR1 gene polymorphisms as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 20533057
- PMCID: PMC2928441
- DOI: 10.1007/s00384-010-0961-2
ABCB1/MDR1 gene polymorphisms as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Objective: To analyse the single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): ABCB1(1236C>T), ABCB1(2677G>T/A), ABCB1(3435C>T) and haplotypes in the ABCB1/MDR1 gene, which could contribute to genetic risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). Disease association between the ABCB1/MDR1 genotype, allele, haplotype frequencies and histological features, such as TNM classification, localization of primary carcinoma, grade of malignancy, histological type of tumour, lymphoid infiltration and vessel invasion were estimated. In this study, the potential role of SNPs of the ABCB1/MDR1 gene as a prognostic marker for CRC was analysed.
Materials and methods: Tumour specimens of 95 patients with CRC were studied. Using automated sequencing or PCR-RFLP method, DNA for three common SNPs of ABCB1/MDR1 was extracted and analysed. The results of genotyping and haplotype analysis with histopathological features, grading and clinical staging of neoplasms were correlated.
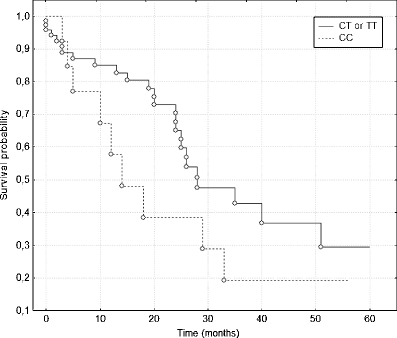
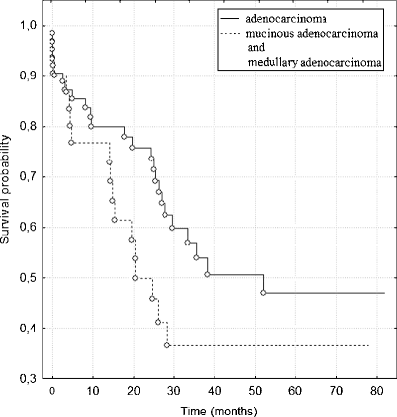
Results: A statistically significant higher frequency of T(1236) allele in T1/T2 (89.7%), M0 groups (81.6%) and I/II clinical staging (82.7%) in comparison with T3/T4 (68.2%), M1 groups (47.4%) and III/IV clinical staging (65.1%) was detected. Furthermore, multivariate analysis according to Cox's proportional hazard model indicated that the T(1236) allele is a good, independent prognostic factor and the presence of this allele decreases the risk of death in comparison with a group without this allele (HR = 0.26; p = 0.0424). In addition, a statistically significant higher frequency of C(3435) allele and significant differences in the C(3435) allele distribution in N1/N2 group (91.7% and 62.5%, respectively) than N0 group (71.2% and 44.9%, respectively) was found. Each of the eight possible haplotypes was noted in M0 or I/II group and only seven in M1 or III/IV group. Haplotype T(1236)-G(2677)-C(3435) only in less advanced CRC subjects (9.6% in I/II and 9.2% in M0 group) was detected. In addition, significant differences in haplotype distributions between M0 or I/II and M1 or III/IV group were found (p = 0.01 and p = 0.05, respectively).
Conclusions: These results suggest association between T(1236) allele and T(1236)-G(2677)-C(3435) haplotype and less advanced CRC, so these genetic markers may play a role as potentially good prognostic factors. Differences in haplotype distributions and degree of clinical staging may suggest that some other potential SNPs, especially in regulatory region of ABCB1/MDR1 gene, may influence P-glycoprotein function and CRC progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ABCB1 gene polymorphisms and haplotype analysis in colorectal cancer.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009 Aug;24(8):895-905. doi: 10.1007/s00384-009-0724-0. Epub 2009 May 5. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009. PMID: 19415305
-
No association between MDR1 (ABCB1) 2677G>T and 3435C>T polymorphism and sporadic colorectal cancer among Bulgarian patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008 Mar;134(3):317-22. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0279-9. Epub 2007 Aug 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17674045 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms and haplotypes in the multidrug resistance 1 gene (MDR1/ABCB1) and risk of multiple myeloma.Leuk Res. 2009 Feb;33(2):332-5. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2008.06.008. Epub 2008 Jul 18. Leuk Res. 2009. PMID: 18639335
-
A synonymous polymorphism in a common MDR1 (ABCB1) haplotype shapes protein function.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 May;1794(5):860-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.02.014. Epub 2009 Mar 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19285158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of CYP3A and ABCB1 single nucleotide polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of calcineurin inhibitors: Part I.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010 Mar;49(3):141-75. doi: 10.2165/11317350-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010. PMID: 20170205 Review.
Cited by
-
MDR1 gene polymorphisms are associated with glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in a Chinese population.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2014 Mar;18(3):196-201. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2013.0374. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2014. PMID: 24387690 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic retinoic acid receptor γ knockdown reverses multi-drug resistance of human colorectal cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Cell Cycle. 2017 Apr 3;16(7):685-692. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1295180. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28272990 Free PMC article.
-
ABCB1 variants C3435T and T129C are not associated with colorectal cancer risk.Afr Health Sci. 2019 Sep;19(3):2476-2483. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v19i3.23. Afr Health Sci. 2019. PMID: 32127820 Free PMC article.
-
The MDR1/ABCB1 gene rs 1045642 polymorphism in colorectal cancer.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Sep 26;16(1):112-117. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2017.70329. eCollection 2020. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32051713 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of detecting multidrug resistance proteins in acute leukemia prognosis and therapy.J Clin Lab Anal. 2013 Jan;27(1):62-71. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21563. Epub 2013 Jan 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2013. PMID: 23292860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

