Age-varying association between statin use and incident Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20533968
- PMCID: PMC3176730
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02906.x
Age-varying association between statin use and incident Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Objectives: To determine whether risk reduction of statins for Alzheimer's disease (AD) varies by age or presence of apolipoprotein E (APOE) epsilon4 allele.
Design: A cohort of cognitively intact elderly participants was assessed biennially for dementia and AD.
Setting: Community based.
Participants: Three thousand three hundred ninety-two members of a health maintenance organization (HMO) aged 65 and older and without dementia.
Measurements: Statin use was identified from the HMO pharmacy database, and proportional hazards models were applied with statin use as a time-dependent covariate to assess the association between statins and AD and the modifying effects of age and the APOE epsilon4 allele.
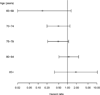
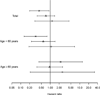
Results: Over an average of 6.1 years of follow-up of 3,099 participants, 263 participants developed probable AD. The adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for statin use was 0.62 (95% confidence interval (CI)=0.40-0.97) for AD in models including demographic characteristics and vascular risk factors as covariates. The strength of the association between statins and AD diminished with age (statin-by-age at entry interaction P=.04); the aHR in those younger than 80 was 0.44 (95% CI=0.25-0.78), versus 1.22 (95% CI=0.61-2.42) for aged 80 and older. The interaction term for statin use-by-APOE epsilon4 was not significant (P=.65).
Conclusion: This enlarged study confirms earlier findings that statin therapy in early old age, but not in late age, may be associated with a lower risk of AD. The relationship between statin use and AD was consistent across APOE genotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Can statins prevent dementia in older adults?J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010 Jul;58(7):1393-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.02907.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010. PMID: 20649690 No abstract available.
-
Exposure to statins in early old age but not in late old age may be associated with a lower risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.Evid Based Ment Health. 2011 Feb;14(1):14. doi: 10.1136/ebmh.14.1.14. Evid Based Ment Health. 2011. PMID: 21266611 No abstract available.
References
-
- Li G, Higdon R, Kukull WA, et al. Statin therapy and risk of dementia in the elderly: A community-based prospective cohort study. Neurology. 2004;63:1624–1628. - PubMed
-
- Rockwood K, Kirkland S, Hogan DB, et al. Use of lipid-lowering agents, indication bias, and the risk of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people. Arch Neurol. 2002;59:223–227. - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–923. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes LU, Gerdes C, Kervinen K, et al. The apolipoprotein epsilon4 allele determines prognosis and the effect on prognosis of simvastatin in survivors of myocardial infarction: A substudy of the Scandinavian simvastatin survival study. Circulation. 2000;101:1366–1371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

