Isothiocyanates induce oxidative stress and suppress the metastasis potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 20534110
- PMCID: PMC2891640
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-269
Isothiocyanates induce oxidative stress and suppress the metastasis potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Isothiocyanates are natural compounds found in consumable cruciferous vegetables. They have been shown to inhibit chemical carcinogenesis by a wide variety of chemical carcinogens in animal models. Recent studies have also shown that isothiocyanates have antitumor activity, inhibiting the growth of several types of cultured human cancer cells. Our previous study showed that PEITC inhibited human leukemia cells growth by inducing apoptosis. However, the effect of isothiocyanates on lung cancer cell metastasis has not been studied. In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effects of BITC and PEITC on metastatic potential of highly metastatic human lung cancer L9981 cells.
Methods: Cell migration and invasion were measured by wound healing assay and transwell chemotaxis assay. Expression of metastasis-related genes was assessed by quantitative RT-PCR and Western blotting. The mechanisms of action were evaluated by flow cytometry, reporter assay and Western blotting.
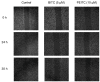
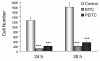
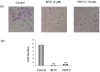
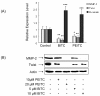
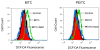
Results: Our data showed that both BITC and PEITC inhibited L9981 cell growth in a dose-dependent manner, the IC50 values were 5.0 and 9.7 microM, respectively. Cell migrations were reduced to 8.1% and 16.5% of control, respectively; and cell invasions were reduced to 2.7% and 7.3% of control, respectively. Metastasis-related genes MMP-2, Twist and beta-catenin were also modulated. BITC and PEITC inhibited cell survival signaling molecules Akt and NFkappaB activation. Moreover, BITC and PEITC increased ROS generation and caused GSH depletion. Pretreatment with NAC blocked BITC and PEITC induced ROS elevation and NFkappaB inhibition.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that BITC and PEITC suppress lung cancer cell metastasis potential by modulation of metastasis-related gene expression, inhibition of Akt/NFkappaB pathway. Induction of oxidative stress may play an important role.
Figures
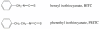
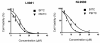
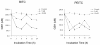

Similar articles
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates the apoptosis of highly metastatic human non-small cell lung cancer cells induced by isothiocyanates.Br J Nutr. 2011 Dec;106(12):1779-91. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511002315. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Br J Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21733335
-
Phenethyl Isothiocyanate (PEITC) and Benzyl Isothiocyanate (BITC) Inhibit Human Melanoma A375.S2 Cell Migration and Invasion by Affecting MAPK Signaling Pathway In Vitro.Anticancer Res. 2017 Nov;37(11):6223-6234. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12073. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29061805
-
Inhibition of benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice by dietary N-acetylcysteine conjugates of benzyl and phenethyl isothiocyanates during the postinitiation phase is associated with activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and p53 activity and induction of apoptosis.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):2-7. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782348
-
Anti-Carcinogenic Glucosinolates in Cruciferous Vegetables and Their Antagonistic Effects on Prevention of Cancers.Molecules. 2018 Nov 15;23(11):2983. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112983. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30445746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional Sources and Anticancer Potential of Phenethyl Isothiocyanate: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Insights.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024 Apr;68(8):e2400063. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202400063. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2024. PMID: 38600885 Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-diagnostic cruciferous vegetables intake and lung cancer survival among Chinese women.Sci Rep. 2015 May 19;5:10306. doi: 10.1038/srep10306. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25988580 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trend and Detailed Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Food Bioactive Compounds against Cancer: A Comprehensive Review with Special Emphasis on Probiotics.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;14(22):5482. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225482. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in Research of Antitumor Mechanisms of Isothiocyanates].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 Mar 20;20(3):213-218. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.03.11. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28302225 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Next-generation multimodality of nutrigenomic cancer therapy: sulforaphane in combination with acetazolamide actively target bronchial carcinoid cancer in disabling the PI3K/Akt/mTOR survival pathway and inducing apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2021 Jul 20;12(15):1470-1489. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28011. eCollection 2021 Jul 20. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34316328 Free PMC article.
-
Prodigiosin-Emerged PI3K/Beclin-1-Independent Pathway Elicits Autophagic Cell Death in Doxorubicin-Sensitive and -Resistant Lung Cancer.J Clin Med. 2018 Oct 3;7(10):321. doi: 10.3390/jcm7100321. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30282915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart BWKP. WHO. World Cancer Report. IARC Press, Lyon, France; 2003.
-
- Ries LEM, Kosary C. Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2002. National Cancer Institute; 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

