DNA topoisomerases and their poisoning by anticancer and antibacterial drugs
- PMID: 20534341
- PMCID: PMC7316379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.04.012
DNA topoisomerases and their poisoning by anticancer and antibacterial drugs
Abstract
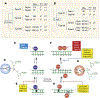
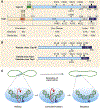
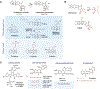
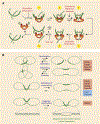
DNA topoisomerases are the targets of important anticancer and antibacterial drugs. Camptothecins and novel noncamptothecins in clinical development (indenoisoquinolines and ARC-111) target eukaryotic type IB topoisomerases (Top1), whereas human type IIA topoisomerases (Top2alpha and Top2beta) are the targets of the widely used anticancer agents etoposide, anthracyclines (doxorubicin, daunorubicin), and mitoxantrone. Bacterial type II topoisomerases (gyrase and Topo IV) are the targets of quinolones and aminocoumarin antibiotics. This review focuses on the molecular and biochemical characteristics of topoisomerases and their inhibitors. We also discuss the common mechanism of action of topoisomerase poisons by interfacial inhibition and trapping of topoisomerase cleavage complexes.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bertrand R, O’Connor P, Kerrigan D, and Pommier Y (1992). Sequential administration of camptothecin and etoposide circumvents the antagonistic cytotoxicity of simultaneous drug administration in slowly growing human colon carcinoma HT-29 cells. Eur. J. Cancer 28A, 743–748. - PubMed
-
- Black MT, and Coleman K (2009). New inhibitors of bacterial topoisomerase GyrA/ParC subunits. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 10, 804–810. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury BJ, and Pucci MJ (2008). Recent advances in bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 8, 574–581. - PubMed
-
- Brangi M, Litman T, Ciotti M, Nishiyama K, Kohlhagen G, Takimoto C, Robey R, Pommier Y, Fojo T, and Bates SE (1999). Camptothecin resistance: role of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC), mitoxantrone-resistance half-transporter (MXR), and potential for glucuronidation in MXR-expressing cells. Cancer Res. 59, 5938–5946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

