Evidence-based management of rapidly progressing systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 20534372
- PMCID: PMC2884006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.berh.2009.12.002
Evidence-based management of rapidly progressing systemic sclerosis
Abstract
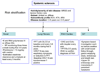
Systemic sclerosis has the highest case-specific mortality of any of the auto-immune rheumatic diseases, as well as causing major morbidity. It is a major clinical challenge and one that has previously provoked substantial nihilism due to the limited therapeutic options available and the perceived lack of evidence for clinical effectiveness of those treatments that are currently in use. However, this situation is changing; there are emerging data supporting efficacy for some treatment approaches for this patient group together with a growing number of exciting potential novel approaches to treatment that are moving into the clinical arena. Some of the recent clinical trials are reviewed and discussed in detail.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Steen VD, Medsger TA., Jr The palpable tendon friction rub: an important physical examination finding in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(6):1146–1151. - PubMed
-
- Nihtyanova SI, Brough GM, Black CM, Denton CP. Mycophenolate mofetil in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis--a retrospective analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2007;46(3):442–445. - PubMed
-
- Shand L, Lunt M, Nihtyanova S, Hoseini M, Silman A, Black CM, et al. Relationship between change in skin score and disease outcome in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: application of a latent linear trajectory model. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(7):2422–2431. - PubMed
-
- Amjadi S, Maranian P, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Wong WK, Postlethwaite AE, et al. Course of the modified Rodnan skin thickness score in systemic sclerosis clinical trials: Analysis of three large multicenter, double-blind, randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(8):2490–2498. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Steen VD, Medsger TA., Jr Improvement in skin thickening in systemic sclerosis associated with improved survival. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(12):2828–2835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

