Regulation of Golgi structure and secretion by receptor-induced G protein βγ complex translocation
- PMID: 20534534
- PMCID: PMC2895111
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003042107
Regulation of Golgi structure and secretion by receptor-induced G protein βγ complex translocation
Abstract
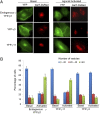
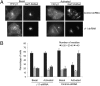
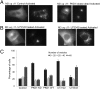
We show that receptor induced G protein betagamma subunit translocation from the plasma membrane to the Golgi allows a receptor to initiate fragmentation and regulate secretion. A lung epithelial cell line, A549, was shown to contain an endogenous translocating G protein gamma subunit and exhibit receptor-induced Golgi fragmentation. Receptor-induced Golgi fragmentation was inhibited by a shRNA specific to the endogenous translocating gamma subunit. A kinase defective protein kinase D and a phospholipase C beta inhibitor blocked receptor-induced Golgi fragmentation, suggesting a role for this process in secretion. Consistent with betagamma translocation dependence, fragmentation induced by receptor activation was inhibited by a dominant negative nontranslocating gamma3. Insulin secretion was shown to be induced by muscarinic receptor activation in a pancreatic beta cell line, NIT-1. Induction of insulin secretion was also inhibited by the dominant negative gamma3 subunit consistent with the Golgi fragmentation induced by betagamma complex translocation playing a role in secretion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akgoz M, Kalyanaraman V, Gautam N. Receptor-mediated reversible translocation of the G protein betagamma complex from the plasma membrane to the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51541–51544. - PubMed
-
- Wilson BS, Komuro M, Farquhar MG. Cellular variations in heterotrimeric G protein localization and expression in rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1994;134:233–244. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson PA, Lock JG, Luke MR, Stow JL. Domains of the TGN: Coats, tethers and G proteins. Traffic. 2004;5:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

